Good illumination or lighting is necessary for all buildings and has three primary aims.
- To promote work and other activities carried out within the building;
- To promote the safety of the people using the building
- To create, in conjunction with the structure and decoration, a pleasing environment conducive to interest of the occupants and a sense of their well-being.
Illumination can transform the night-time appearance of a building or landscape. The aesthetics, usability and desirability of a structure or place can be increased by good illumination design.
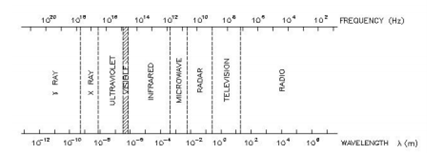
Electromagnetic radiation spectrum
Basic Terminology and Definitions
In illumination, four main units are used to describe light and its effects
Luminous flux : Luminous flux (Φ) is the quantity of the energy of the light emitted per second in all directions. unit :- lumen (lm).
Luminous intensity : Luminous intensity (I) is the ability to emit light into a given direction, or it is the luminous flux that is radiated by the light source in a given direction within the unit of the spatial angel. unit :-candela.
Illuminance : Illuminance (E) is the total luminous flux incident on a surface, per unit area. unit :- lux (lx).
Luminance : Luminance (L) is the luminous intensity emitted by the surface area of 1 cm² (or 1 m²) of the light source.
E=Φ/A
A= Illuminated surface (m2)
Φ = Luminous flux
E = Illuminance
L=I/A
A = Illuminated surface (m2)
I = Luminous intensity
L = Luminance
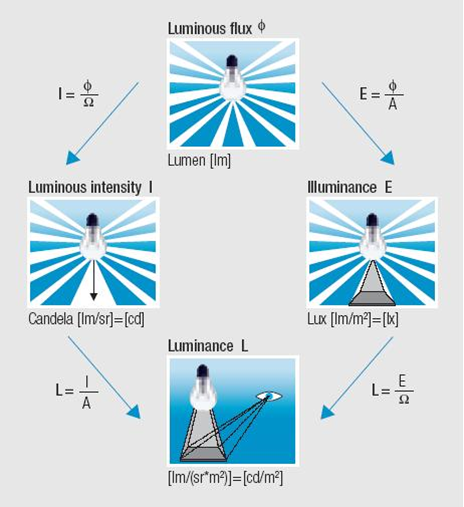
Ω = solid angle into which luminous flux is emitted
A = area hit by luminous flux
All four Light units can be described as psychophysical as they are combination of human response and physical units of power.
Laws of Illumination
The Inverse Square Law of Illuminance
The Cosine Law of Illuminance / Lambert’s Cosine Law
Laws of Reflection and Refraction
Identification of Lighting Requirements
Design of the lighting system : lumen method
Classification of lighting system
Software for illumination calculation in project
Indian Standards (IS CODE) for lighting
| IS CODE | Title |
| SP 72 : 2010 | National Lighting Code |
| IS 2440 : 1975 | Guide for daylighting of buildings (second revision) |
| IS 3646 (Part 1) : 1992 | Code of practice for interior illumination: Part 1 General requirements and recommendations for working interiors (first revision) |
| IS 7662 (Part 1) : 1974 | Recommendations for orientation of buildings : Part 1 Non-industrial buildings |
| IS 11907 : 1986 | Recommendations for calculation of solar radiation on buildings |
| SP 32 : 1986 | Handbook on functional requirements of industrial buildings (lighting and ventilation) |
| SP 41 : 1987 | Handbook on functional requirements of buildings other than industrial buildings |
Reference Book
| S. No. | Title |
| 1 | Lighting By D.C. Pritchard |
| 2 | IESNA Lighting Handbook |
| 3 | FHWA Lighting Handbook August 2012 |
| 4 | ZUMTOBEL Lighting Handbook |
FD Architect Community Forum Discussion
- Illumination – introduction
- Basic Terminology and Definitions
- Laws of Illumination The Inverse Square Law of Illuminance Illuminance (E) at any poi
- Laws of Reflection and Refraction
- Visual efficiency & comfort
- Day lighting
- Components of Daylight Factor
- Artificial Lighting Design
Download Study Notes PDF
Register as member and login to download attachment use this only for Educational Purpose
Disclaimer
Information on this site is purely for education purpose. The materials used and displayed on the Sites, including text, photographs, graphics, illustrations and artwork, video, music and sound, and names, logos, IS Codes, are copyright
22 thoughts on “Illumination in architecture”