Timber is one of the most important building materials, Timber is self renewing and trees have always exerted significant effects on people and the environment.
Timber is an essential component of building constructed in all other materials –generally as scaffolding or levers or Specifically as centering for masonry , formwork for lining for concrete or fixing for steelwork.
Hardwood
Hardwood is produced by trees that have broad leaves – lose them in winter – reproduce them in spring. Species are oak, pecan, walnut, ash, cherry, birch, etc. Slow growth.
Softwood
Softwood is the type that comes from trees that have needles, are evergreen, do not lose them in winter. Species include pine, fir, spruce, larch, cedar, etc. Fast growth. Much more plentiful than hardwoods.
Qualities of Wood
The material wood is:
- Strong
- Light
- Easily handled, worked, & shaped
- Fastened quickly & economically
- Recyclable
- Biodegradable
- A renewable resource
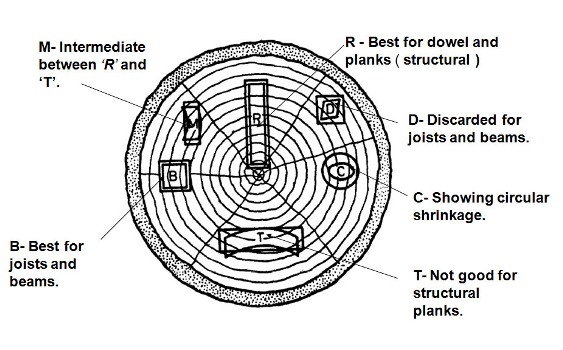
Sketch showing differential shrinkage in the tangential and radial directions as per is code 3629-1986
Undesirable Characteristics of Wood
- Not perfectly straight
- Affected by moisture
- Has growth defects
- But can be protected from:
- Splitting & warping
- Burning
- Decaying
- Attack by Insects
Tree Composition

Tree Growth
Springwood (earlywood)
- Faster growth
- Cells larger and less dense
Summerwood (latewood)
- Slower growth
- Cells smaller and denser
Construction Uses for Wood
- Structural Framing
- Subfloors and Roof Sheathing
- Finish Siding ( generally all softwood)
- Finish cabinetry, trim, & paneling (generally hardwood)
Engineered Wood
Wood used in construction includes products such as :
- chipboard,
- hardboard,
- medium-density fibreboard (MDF),
- oriented strand board (OSB).
- Such wood derivatives are widely used: wood fibers are an important component of most paper, and cellulose is used as a component of some synthetic materials. Wood derivatives can also be used for kinds of flooring, for example laminate flooring.
Engineered Wood Panel Products
Why Panelize?
- More “controlled” product
- Efficient use of forest products
- Increase labor productivity
Types
- Plywood panels
- Composite panels
- Non veneered panels
Veneered Panels – Plywood
- Thin layers of veneer glued together
- Odd number of veneers
- Alternating direction of veneers
- Face veneers parallel
- Size: 4’x8’ panels
- Thickness: ¼” to 1”
- Plywood came into wide use in the 1950s because of increase in labor cost.

Non-veneered Panels
- Oriented Strand Board (OSB)
- Waferboard
- Particleboard
- Fiberboard

Oriented Strand Board (OSB)
- Has long strand-like wood particles
- Grain orientation alternates (3-5 layers)
- Glued and compressed
- Strongest of the Non-veneered
- Uses: Sheathing for floor, roofs, & siding

Waferboard & Particleboard
Waferboard
- Weak material
- Large wafer-like particles – No orientation
- Uses: Low moisture areas
Particleboard
- Weak material
- Small wood particles
- No orientation
- Uses: Low moisture areas

Both products are inferior where strength is required and moisture is present.
Wood Polymer Composite Planks
“Artificial Wood” not in wide general use because it is new and untested. Probably will be used extensively in the future because of its stability, durability to weather, and resistance to insects.
Advantages:
- Decay Resistance
- Easy Workability

Constructing the Wall Framing
- Build on the Platform & Tilt-up or
- Build in Place

Wall Framing Layout, Framing Member Size & Spacing
Loads Vertical & Lateral
- Floor Loads, # of Stories, Roof Loads, Wind, Quake
- Minimum – Code Requirements
Attachment of:
- Exterior and
- Interior Finishes
Opening Locations – Doors & WindowsInsulation Requirements (may elect to use ‘deeper framing to accommodate thicker insulation)
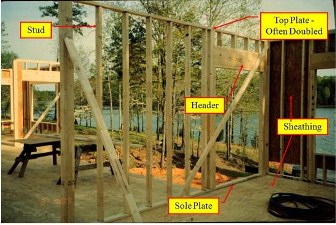
Wall Sheathing
Materials:
- Typically – OSB or Plywood
- Insulating Sheathing – (no structural qualities)

Sheathing Purposes:
- Joins & stabilizes the structure
- Resists uplift
- Resists wracking- Resists lateral forces
- Provides surface for finish material

Roof Profiles
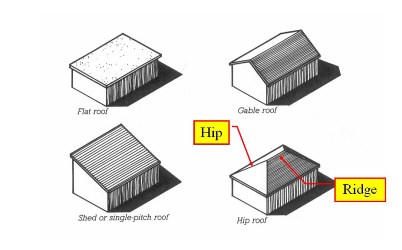
- Flat Roof
- Single Pitch
- Gable Roof
- Hip Roof




Information on this site is purely for education (students / users) purpose. The materials used and displayed on the Sites, including text, photographs, graphics, illustrations and artwork, video, music and sound, and names, logos, IS Codes, are copyrighted items of respective owners. They are provided here just for refrence/information.
For your views and discussions Register in FDAchitects Forum …