- FORUM
- PROJECTS
- ABOUT US
- RESOURCES
- CONTACT US
- FORUM
- PROJECTS
- ABOUT US
- RESOURCES
- CONTACT US
Bricks
Brick was the first building material to be made by man There is deep satisfaction in constructing a building from units scaled to a man’s hand. Bricks has been used consistently from Egyptians to modern day American buildings.
Types of Bricks.
Sand Lime Brick
- These are made by using mix of lime and sand that ratio is 1:8.
- Brick will curing in autoclave in 8 hours
- That curing will produced high compressive strength and more hard brick.
- These used for wall that will exposed in water with higher compressive strength

Mortar Brick
- Made with mix of cement, sand and water.
- These use steel or wood mould to form it.
- Normally, the design do not produce a good appearance and come out with rough surface.

Fly Ash Bricks

Clay Bricks
Classified in 3 groups : normal brick, face brick, and engineering brick.
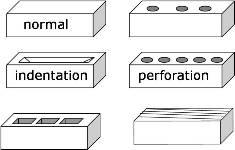
Normal brick – These are ordinary bricks which are not designed to provide good finished appearance or high strength. They are therefore in general and cheapest bricks available.
Face brick – These are designed to give attractive appearance, hence they are free from imperfection such as cracks. It’s produces in variety of color. It’s no need plaster when used as wall.
Engineering Brick – These are design base on engineering characteristic. It’s designed primarily for strength and durability. They are high density and well fired. Normally, it’s will be used as retaining wall, load bearing wall and sewerage.
Brick Masonry terms
Bonding – the method of laying masonry units in a wall in a regular pattern for strength & generally in such a way that there are no continuous vertical joints in successive courses.
Bricks Bonding
There are three types of brick bondings viz;
Flemish Bond Alternate bricks are placed as header and stretcher in every course. Each header is placed centrally between the stretcher immediately above and below. This is not as strong as the English bond at 1 brick thick.
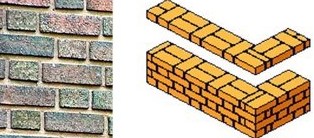
English Bond Alternative courses of headers and stretchers; one header placed centrally above each stretcher. This is a very strong bond when the wall is 1 brick thick (or thicker). One of the strongest brickwork bond patterns.
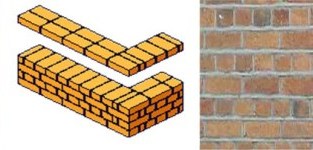
Stretcher Bond Easiest bond to lay & minimizes the amount of cutting required Originally used for single brick walls, now called 1/2 brick walls it became the obvious choice for cavity walls as less cutting was required.
Brick Manufacturing Processes
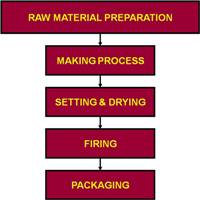
1. Raw Material Preparation

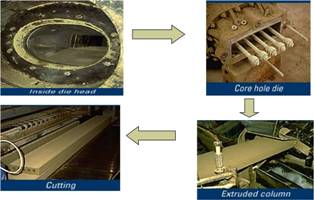
2. The Making Process
Clay will be grinded with 15% of water.
The clay will be pushed through the mould based on the shape.
After that, clay will cut to get a standard size of brick using wire.
Sometimes, bricks will produced using big mould that clay will be press that using hydraulic machine (this method, clay will grind 10% of water) or without hydraulic press (with 30% of water)
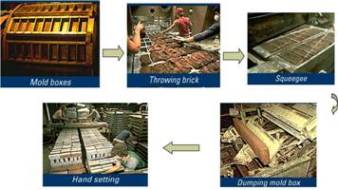
3. Setting and Drying
After bricks in form, indentation or perforation to the bricks.
Wet unit bricks will be drying in space or room with control temperature to make sure the bricks in complete dry.
4. Firing
Dry bricks, was compile in kiln to firing process with 600oC (temperature).
The main stage of firing are:
- 100 oc evaporation of water
- 400 0c burning of carbon and sulfur
- 900 – 1000 0c Strengthen the bricks
Maintaining control of the temperature is most important
- Too rapid fire – over burning the external layer
- Too slow – seriously impairs the strength and durability
Stronger brick such as Engineering Brick, are normally fired at higher temperature.
5. Packaging
- After exiting the kiln, the brick is allowed to cool prior to handling.
- Proper sorting and packaging of the brick after burning is extremely important.
- Broken, twisted and otherwise mechanically defective brick are discarded at this stage.
- Brick color and range is carefully monitored to assure a quality product.
Advantages of Brick
- Brick will not burn, buckle or melt.
- Brick will not rot and allow Termites to invade.
- Brick will not rust and corrode.
- Brick will not dent.
- Brick will not fade from the Sun’s UV Rays.
- Brick will not be damaged by high winds, rain or hail.
- Brick will not require constant maintenance.
- Brick will not devalue.
- Brick will not limit your personal expression.
- Brick will not limit your design options.
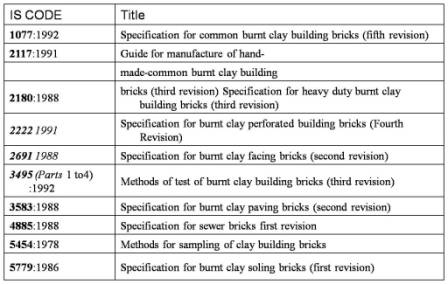
Indian Standards (IS CODE) for bricks
Objective To control quality of the brick
Brick Work
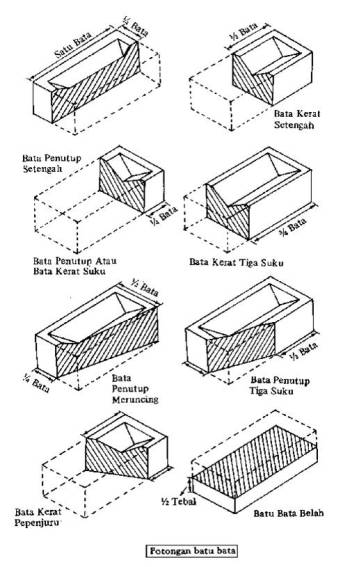
Brick shape in brick work
To produce the variety of arrangement or special purpose in brick work
Brick Test
Six Brick Test
- Compressive Strength Test
- Water Absorption Test
- Efflorescence Test
- Initial Rate of Absorption Test
- Moisture Expansion Test
- Salt attack resistance Test
Compressive Strength Test
Fairly obviously, this is the ability of the masonry unit (brick or block) to resist crushing loads, eg the weight of the roof that the wall is supporting, plus the weight of the wall itself. The designer of the structure needs to be sure that the masonry unit will be able to carry the load being placed upon it, including any live loads.
The bricks, when tested in accordance with the procedure laid down in IS 3495 (Part 1) : 1992 shall have a minimum average compressive strength for various classes as given in TABLE 4.1 of IS 1077 : 1992
Water Absorption Test
A standard soaking-in-water test can determine the porosity of bricks, which can then be used as an indication of the potential for the development of problems related to the penetration of salts and other materials into the units, such as salt attack and efflorescence.
The bricks, when tested in accordance with the procedure laid down in IS 3495 (Part 2) : 1992 after immersion in cold water for 24 hours, water absorption shall not be more than 20 % by weight up to class 12.5 and 15 % by weight for higher classes.
Efflorescence Test
Efflorescence is a deposit of salts, usually white, on the surface of bricks and blocks after being laid. The salts usually come from ground water or out of the mortar, but may come from within the masonry units themselves.
This test predicts the likelihood that the units will display such unsightly deposits from salts that they already contain.
Forum Threads
The bricks when tested in accordance with the procedure laid down in IS 3495 (Part 3 ) : 1992 Standard Mark. the rating of efflorescence shall not be more than ‘moderate up to class 12.5 and ‘slight’ for higher classes Information on this site is purely for education (students / users) purpose. The materials used and displayed on the Sites, including text, photographs, graphics, illustrations and artwork, video, music and sound, and names, logos, IS Codes, are copyrighted items of respective owners. They are provided here just for refrence/information.
For your views and discussions Register in FDAchitects Forum …