- FORUM
- PROJECTS
- ABOUT US
- RESOURCES
- CONTACT US
- FORUM
- PROJECTS
- ABOUT US
- RESOURCES
- CONTACT US
Glass
Glass
Glass is a state of matter, not a particular substance. It is an amorphous solid that is cooled to rigidity without crystallizing.
Types of Glass
Sheet Glass
The basic procedure used for manufacturing sheet glass is drawing First glass is produced in molten state . A bait ( steel rod) is inserted into molten glass and as it has high viscosity , it adhere to rod . With bait the glass can be drawn vertically upwards ( between jets of flame ) by rollers .
Plate Glass Plate glass is made by casting glass horizontally and polishing it. However in about 1922 , the continuous rolling methods to produced plate glass were introduced. In this process the molten glass is flowed horizontally through an opening into the water cooled forming rolls.
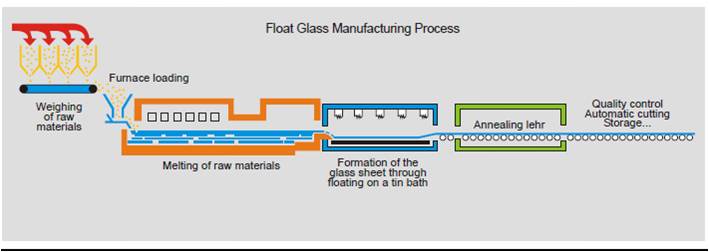
Float Glass Glass has been a major building component for centuries and the basic composition of glass has changed very little from its conception as sheet glass to today’s state-of-the-art float glass.
Solar control Glass
Glass in its basic form is also available as a coated glass wherein the coating is done during the float glass manufacturing process. These coatings generally known as Hard Coatings or pyrolytic coatings are very durable and are quite suitable for further processing like tempering, heat-strengthening, laminating, insulating etc.
Guidelines On Use of Glass in Buildings – Human Safety
In the modern lifestyle, increased Glass use in buildings offers many advantages. Those who spend more time indoors have intuitively understood benefits of improved daylight and vision on human psychology and health, and recentresearch findings underscore these indisputably. Howeverthisincreased use of glassin Indian buildingsis not without risks. Wrong selection of glass type is widespread and does result in increased heat gain/loss in buildings and the higher risk of injuriesto humans. These are side affectsthat the building industry is only recently beginning to recognize.
Recognizing the gravity of the problem and uncertainty faced by the Engineers, Architects and users, the guidelines for selection of appropriate safety glass suitable for a particular location has been brought out.
Clear Float Glass
Basic float glass is manufactured by melting sand. Other ingredients such as soda ash, limestone and salt cake are added to lower the melting temperature of silica and promote optical clarity of the finished glass product. Mixed batch of above materials is heated to a temperature of about 1650° C and formed into large flat sheets by floating molten glass on molten tin, thus giving it precise flatness and transparency..
Tinted Float Glass
It is basic float glass that has been coloured by the addition of metal oxides into molten glass. Body tinted glass possesses filtering properties that help reduce eye strain due to the dazzling effects of sun glare. Its absorption properties help diminish energy transmissions through glass when exposed to strong sunlight. Variations in the thickness of the glass would yield different performance in terms of light and solar transmission. Although darker shades reduce the amount of heat being transmitted to the interiors, they also reduce the amount of daylight being transmitted at the same time.
Hard Coated Float Glass
It is also a basic clear or body tinted float glass which has been coated with a thin metallic film in the molten stage to reflect heat (Reflective) or to reduce energy emission (Low-E) and to allow light in. These are discussed in more detail under the heading “Solar Control Glasses”. Float glass is monolithic, highly transparent glass which can be used as such or further processed to bring a combination of function and beauty to both architectural applications and speciality uses.
Patterned, Figured or Rolled Glass
It is a decorative and translucent glass with figures or patterns on one face or both surfaces. In addition to diffusing light and obstructing visibility from the outside, the figures soften the interior lighting. It is manufactured by a method similar to float glass wherein the molten glass is passed through rollors instead of floating on a molten tin bath. These metallic rollors are engraved with some patterns or designs, which are cast into the formed glass. The glass itself is quite low priced and can be used in most applications for lighting but no see through. This type of glass is usually more brittle or fragile and less convenient to clean.
Wired Glass
Wired glass is a glass in which wire mesh has been incorporated during its production. There are two kinds of wired glass:
- Wired Float Glass
Wired Float Glass is formulated for fire protection performance. In case of fire, the glass cracks but broken pieces tend to remain in the sash for a short time, rather than fall out, restricting the spread of flame and smoke for some time. It is one of the most cost effective glazing materials when a nominal fire protection is required in windows, doors and partitions.
- Figured Wired Glass.
Figured Wired Glass is not see through, is much inferior and not fire rated.
Extra Clear Glass
Though glass is transparent, it does possess a slight greenish tint due to the presence of some impurities, mainly iron. Glass is made basically of silica and during the manufacturing process, inspite of proper cleaning of materials, impurities remain. These impurities are there mainly in the sand and lead to the glass having a slight greenish tint. In display counters and windows, this greenish tint interferes with the true representation of colour and shine. Now there is a glass which is purer and remarkably clear. This extra clear glass is used for a sparkling display of expensive materials like jewelry, watches, crystal ware, fine fabrics, art ware etc. This glass when used for making glass furniture with edge polishing gives a great edge shine, thereby enhancing the aesthetic appeal. Extra clear glass is also used in photovoltaic modules and scientific applications where a higher light or solar transmission is required.
Soft Coating
A secondary process, is a metallic coating on glass by process in a vacuum atmosphere. Multiple coatings can be applied for better thermal performance in a variety of colour options. Soft coated glass cannot be tempered after coating and needs to be protected inside a double glazing or laminated. Soft coating with additional protective coating, known as Medium Coating enables the glass to be processed further. It has the thermal performance of soft coated glass but can be tempered after coating and can also be single glazed with coated side exposed to the interiors only.
Solar Reflective Glass
comprises of a sheet of clear or coloured float glass that has been coated with a thin layer of metal oxide on a single side of the glass. Solar reflective glass has the ability to reflect some and absorb some part of the solar radiation. The range of coatings, colours and thickness offers an extensive choice of levels of solar protection. Due to the coating of metal oxides on the glass, solar reflective glass is widely applied as an aesthetic product in architecture for its highly reflective surface and its wide palette of colours.
An exceptional property of solar reflective glass is that the coating of metal oxides on the glass can be achieved without affecting the transparency of the glass. Solar reflective glass can be used in a number of combinations employing other glass technologies to enhance its performance.
Low-E glass
Is an innovative coated glass that prevents heat from escaping during the winter and reduces the amount of heat that enters a building in the summer. It is used widely in residential, commercial and industrial applications. Similar to solar reflective glass, low-emissivity glass (commonly known as low-e glass) relies on special coatings to achieve its high performance in principle. Low-E glass is able to selectively reflect the invisible long-wave infrared or heat while letting the visible light in.
The low-e coating allows for exceptionally high visible light transmission of up to 70% as compared to 79% in clear glass while sustaining high performance in solar insulation by reducing infrared transmission and solar heat gain. The use of low-e glass can substantially reduce the heat gain within a building and hence its energy consumption for air-conditioning. Low-E coating on tinted glass would reduce glare and improve its thermal performance.
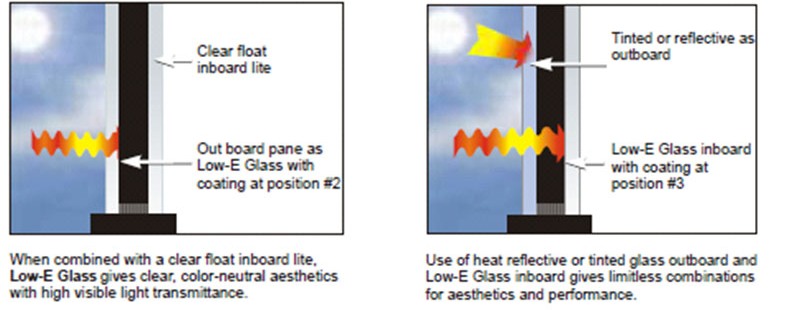
DGU (DOUBLE GLASS UNITS ): low-e glass can also be used in DGU units. When short-wave infrared energy strikes the tinted exterior ply glass, it is absorbed and converted into long-wave infrared or heat.
By applying a low-e coating to the second surface of the DGU unit, the heat is re-radiated back to the exteriors, thus reducing the heat gain potential into the building interior.
Tempered Glass
Is an extremely strong glass which has been thermally heat treated to induce compressive stresses of 11000 to 20000 psi on the surfaces and edge compression of not less than 9700 psi.
Tempering Process: Tempered glass is made on state-of-the-art, electrically heated horizontal furnaces, which heat the glass to a uniform temperature of approximately 700°C. Ceramic rolls convey the glass through the furnace at speeds regulated to ensure temperature uniformity and minimal optical distortions. When the glass exits from the furnace, it is rapidly cooled by a series of air nozzles. This rapid cooling puts the glass surface into a state of compression, with the center core in tension. In the Final Stress Distribution, the sum of the forces in compression equals the forces in tension.
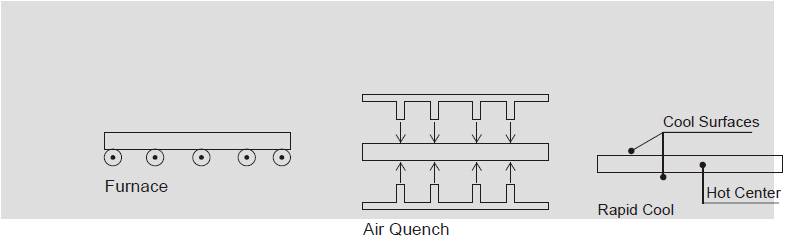
Characteristics of Tempered Glass
- Strength: Toughened (or Tempered Glass) is four to five times stronger than its equivalent thickness of normal annealed float or sheet glass.
- High Thermal Shock Strength: Tempered Glass provides greater thermal strength. lt offers increased resistance to both sudden temperature changes and temperature differentials up to 250°C compared to normal annealed glass which can withstand temperature differentials up to 40°C only.
Heat Strengthened Glass
Heat strengthened glass is a semi tempered glass which has been strengthened thermally by inducing a surface compression of 6000 to 9000 psi as compared to a range of 11000 to 20000 psi in case of fully tempered glass.
In heat strengthening process electrically heated horizontal furnace, which heats the glass to a uniform temperature of approximately 660° C. Ceramic rolls convey the glass through these furnaces at speeds regulated to ensure temperature uniformity and minimal optical distortions.
Ceramic Printed Glass
Also known as silk screened glass is a glass which has been printed by a silk screen with a glass enamel before the glass is tempered or heat strengthened.
On tempering or heat strengthening, the glass enamel fuses into the glass surface and becomes a permanent coating which cannot be damaged or removed by cleaning or scrubbing etc

Information on this site is purely for education purpose. The materials used and displayed on the Sites, including text, photographs, graphics, illustrations and artwork, video, music and sound, and names, logos, IS Codes, are copyrighted items of respective owners. They are provided here just for refrence/information.
Forum Threads
For your views and discussions Register in FDAchitects Forum …