- FORUM
- PROJECTS
- ABOUT US
- RESOURCES
- CONTACT US
- FORUM
- PROJECTS
- ABOUT US
- RESOURCES
- CONTACT US
Plastics
Plastics are macro molecules, formed by Polymerization and having the ability to be shaped by the application of reasonable amount of heat and pressure or some other form of force.
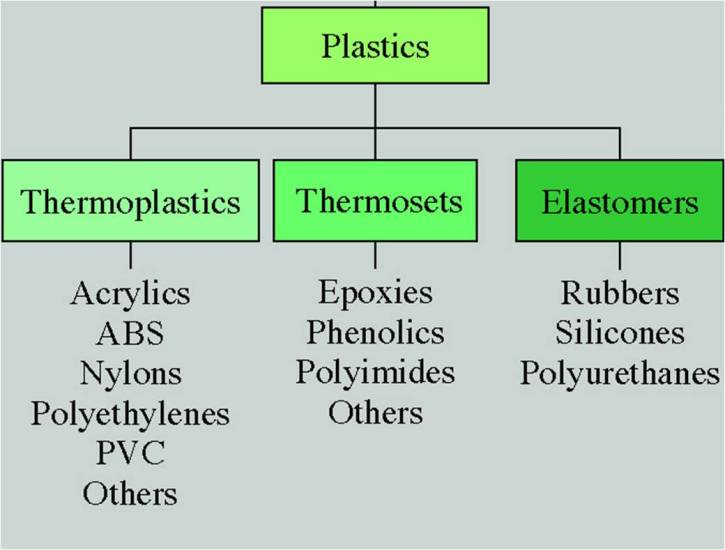
Types of PlasticThermoplastics
Reversible in phase by heating and cooling. Solid phase at room temperature and liquid phase at elevated temperature.
Thermosets
Irreversible in phase by heating and cooling. Change to liquid phase when heated, then follow with an irreversible exothermic chemical reaction. Remain in solid phase subsequently.
Elastomers Elastic in behaviour under load also know as Rubbers.
Thermoplastics
General properties: low melting point, softer, flexible. Typical uses: bottles, food wrappers, toys, …
Examples:
Polyethylene (or polythene) : Flexible use in packaging, electrical insulation, milk and water bottles, packaging film
- Polypropylene: Stiff and hard and coarser then the polyethylene of low density , use carpet fibers, automotive bumpers, microwave containers, prosthetics
- Polyvinyl chloride (PVC): Rigid ,Tough and elastic to feel, use in electrical cables cover, credit cards, car instrument panels
- Polystyrene: Soild , glass clear and sparkling , use in disposable spoons, forks, Styrofoam™
- Acrylics (PMMA: polymethyl methacrylate): Glass clear , somewhat brittle sound when tapped , use in paints, fake fur, plexiglass
- Polyamide (nylon): high density polythene but smoother to feel use in textiles and fabrics, gears, bushing and washers, bearings
- PET (polyethylene terephthalate): use in bottles for acidic foods like juices, food trays
- PTFE (polytetrafluoroethylene): use in non-stick coating, Gore-Tex™ (raincoats), dental floss
Thermosets
General properties: more durable, harder, tough, light. Typical uses: automobile parts, construction materials.
Examples:
- Malemine formaldehyde (formica ) use in laminates
- Phenolics ( bakelite) : bottle caps , bonding plywood , glues
- Unsaturated Polyesters: lacquers, varnishes, boat hulls, furniture
- Epoxies and Resins: glues, coating of electrical circuits,
- composites: fiberglass in helicopter blades, boats, …
Elastomers
General properties: these are thermosets, and have rubber-like properties. Typical uses: medical masks, gloves, rubber-substitutes
Types of Rubber :
- Natural rubber : It is natural product form rubber tree , The milk form rubber trees called latex is collected at rubber plantations
- Synthetic rubbers: this is a polymer and it is manufactured by chemical process of polymerization
Synthetic rubber examples
- butadiene rubber
- butyl rubber
- chloroprene rubber
- ethylene-propylene rubber
- isoprene rubber
- nitrile rubber
- Polyurethanes : mattress, cushion, insulation, toys
- Silicones : surgical gloves, applications in joint seals
- styrene-butadiene rubber (SBR) :
- thermoplastic elastomers
Polymerization Of Plastics
The process of producing resins of plastics is called polymerization. thus polymerization is the process of combining molecules of compounds to form another complex molecule.
- By addition polymerization :
In this process the same molecules are made to form a bigger molecule . Thus , in the preparation of polythene (polythene), ethane , a carbon compound , is passed under pressure into an inert insolvent containing a special catalyst (a Ziegler catalyst named after the inventor of the process) to form a polymer A high density form of ethane called polyethane or polythene with a softening point of 130° C is produced. We are familiar with polythene sheets in our everyday life
- By condensation polymerization:
in this process a large number of identical or different molecules combine and a low molecular substance is removed . For example terylene is a condensation polymer It is synthesized from alcohol ,ethene, glycol and a benzene derivative when heated together , eliminates molecules of water between them and become terylene . Nylon is another example of a condensation polymer .
- By Co-polymerization:
In this process , two or more different monomers are added together to from a polymer . Phenol formaldehyde is produced by reaction of phenol and formaldehyde.
Silicone
- Silicones are polymers that include silicon together with carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, and sometimes other chemical elements. Some common forms include silicone oil, silicone grease, silicone rubber, and silicone resin
- Silicones are inert, synthetic compounds with a wide variety of forms and uses. Typically heat-resistant and rubber-like, they are commonly used in cookware, medical applications, sealants, adhesives, lubricants, insulation.
- COMPANY which manufacture silicone are : Dow Corning ,GE , Dr Fixit
Melamine
- Melamine resin or melamine formaldehyde (also shortened to melamine) is a hard, thermosetting plastic material made from melamine and formaldehyde by polymerization.
- Melamine resin is the main constituent of high-pressure laminates, such as Formica and Arborite,and of laminate flooring.
- Melamine-resin tile wall panels can also be used as whiteboards.
- Melamine resin is used in kitchen utensils and plates (such as Melmac).
Phenol formaldehyde (PF) resins
- Phenol formaldehyde resins (PF) include synthetic thermosetting resins such as obtained by the reaction of phenols with formaldehyde.
- Phenolic resins are mainly used in the production of circuit boards.
- They are better known however for the production of molded products including pool balls, laboratory countertops, and as coatings and adhesives.
- In the form of Bakelite, they are the earliest commercial synthetic resin.
Information on this site is purely for education (students / users) purpose. The materials used and displayed on the Sites, including text, photographs, graphics, illustrations and artwork, video, music and sound, and names, logos, IS Codes, are copyrighted items of respective owners. They are provided here for educational use only.
For your views and discussions Register in FDAchitects Forum …