- FORUM
- PROJECTS
- ABOUT US
- RESOURCES
- CONTACT US
- FORUM
- PROJECTS
- ABOUT US
- RESOURCES
- CONTACT US
Precast Construction
The concept of precast (also known as “prefabricated”) construction includes those buildings where the majority of structural components are standardized and produced in plants in a location away from the building, and then transported to the site for assembly.
Features
The main features of this construction process are as follows:
- The division and specialization of the human workforce.
- The use of tools, machinery, and other equipment, usually automated, in the production of standard, interchangeable parts and products.
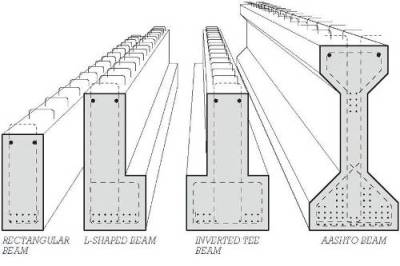
Precast Reinforced Concrete
Precast reinforced concrete floor systems
It requires little or no temporary support , it is consist of
- Precast reinforced concrete (PRC) floor beams
- PRC planks
- PRC tee beams or beam
- PRC infill blocks on which a screed or structural concrete topping is spread



Precast hollow floor units
These large precast reinforced concrete, hollow floor units are usually available in following dimension
Precast concrete floors are designed primarily to eliminate shuttering and wet concrete pouring processes that make the construction of an in situ cast reinforced floor a slow procedure.
The advantage of the completely precast floor is that it can be constructed rapidly and readily it provides a platform from which further work on the building can immediately go on.
A disadvantage is that it is less easy to provide a rigid connection between the precast unit and the supporting beams or wall. The precast beam or the precast rib and filler block construction must act together as a single unit to horizontal actions (wind, earthquake).
Hollow core slabs stacked at the precasting plant.
Precast Concrete Columns And Wall Panels
- Provide support for beam and slab elements.
- Since these elements carry mainly axial loads with little bending force, they may be conventionally reinforced without prestressing.
- Or, long, slender multistory elements may be prestressed to provide resistance to bending forces during handling and erection (columns at right).



- Wall panels can be ribbed, to increase their vertical span capacity while minimizing weight, or formed into other special shapes.
- Precast concrete wall panels may be solid hollow, or sandwiched (with an insulating core).
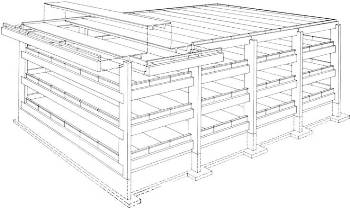
Assembly Concepts For Precast Concrete Buildings
- Vertical support can be provided by precast columns and beams (above), wall panels (below), or a combination of all three.
- The choice of roof and floor slab elements depends mainly on span requirements.
- Precast slab elements are frequently also used with other vertical loadbearing systems such as sitecast concrete, reinforced masonry, or steel.
Precast Reinforced Concrete Wall Frames
Precast concrete wall frames were used extensively in Russia and northern European countries in the construction of multi-storey housing where repetitive units of accommodation were framed and enclosed by large precast reinforced concrete wall panels that served as both external and internal walls and as a structural frame.
Assembly Concepts For Precast Concrete Buildings
1. Precast concrete structure consisting of solid wall panels and hollow core slabs.



2. A single story warehouse consisting of double tees supported by insulated sandwich wall panels.
3. A parking garage structure consisting of precast double tees supported by inverted tee beams on haunched columns.
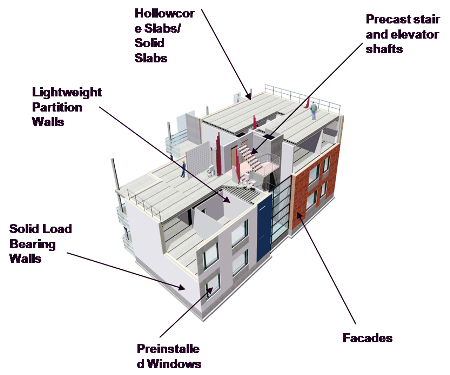
Precast Structural Elements
- Walls
- Load Bearing Walls
- Non Load Bearing Walls
- Sandwich Walls
- Slabs
- Solid Slabs
- Hollow Core Slabs
- Filigree Slabs (Semi Precast)
- Facades
- Beams
- Columns
- Stair & Elevator shafts
Nearly all structural elements can be made using Pre Cast Technology
Precast Types
There are generally following types of precast panels or slabs used as part of building envelopes:
- Cladding or curtain walls
- Load-bearing wall units
- Shear walls
- Formwork for cast-in-place concrete
- Solid Slab
- Hollow core Slab
- Filigree Slab
Precast Panel : Cladding or curtain walls

Precast concrete panels do not transfer vertical loads but simply enclose the space. They are only designed to resist wind, seismic forces generated by their own weight, and forces required to transfer the weight of the panel to the support.
Common cladding units include
- wall panels
- window wall units
- spandrels
- mullions
- column covers
These units can usually be removed individually if necessary.
Precast Panel : Load-bearing wall units

Load-bearing wall units resist and transfer loads from other elements and
cannot be removed without affecting the strength or stability of the building.
Typical load-bearing wall units include solid wall panels, and window wall
and spandrel panels.

Precast Panel : Shear walls
Precast concrete shear wall panels are used to provide lateral load resisting system when
combined with diaphragm action of the floor construction. The effectiveness of precast shear
walls is largely dependent upon the panel-to-panel connections.
Precast Panel : Performance Issues
Thermal Performance
The amount of insulation placed in the cavity or within the backup wall
Moisture Protection
The most common moisture protection system used with precast concrete wall systems is a barrier system incorporating an adequate joint seal.
Fire Safety
Precast concrete wall systems are not considered to provide any improvement in fire safety over cast-in-place concrete.
Acoustics
A precast concrete wall system and cast-in-place facade will provide similar performance regarding sound transmission from the exterior to the interior of the building. However, distressed and open joints between panels can provide a condition in which sound transmission to the interior may be increased.
Material/Finish Durability ,Maintainability
The most important maintenance item for precast panels is the sealant in joints and protection system, if used. If a sealer or concrete coating has been used for aesthetics or to minimize moisture penetration into the panel, the sealer or coating will require reapplication.
Forum Threads
Disclaimer
Information on this site is purely for education (students / users) purpose. The materials used and displayed on the Sites, including text, photographs, graphics, illustrations and artwork, video, music and sound, and names, logos, IS Codes, are copyrighted items of respective owners. They are provided here just for refrence/information.
For your views and discussions Register in FDAchitects Forum …
1 Comment
Shop high-quality concrete wall panels online in India for your construction needs. Our durable and versatile panels offer strength and stability, perfect for various projects. Browse our selection and order now for reliable delivery to your doorstep. Enhance your construction endeavors with top-notch concrete panels, sourced and delivered with utmost convenience. Invest in quality materials for lasting results!