- FORUM
- PROJECTS
- ABOUT US
- RESOURCES
- CONTACT US
- FORUM
- PROJECTS
- ABOUT US
- RESOURCES
- CONTACT US
Case studies that address the challenges in the water sector faced by the cities today, including scarcity of water, management of water resources, high water losses, water for the poor, among others. 21
INTEGRATED WATER MANAGEMENT POLICY:
implementation of an integrated water management by means of a comprehensive policy framework with a focus on conservation and optimum resource utilization.
Singapore – Integrated water resource management: Singapore has adopted an integrated approach to water resource management, enforced by a national water policy and water master plan. The implementation of programs is carried out by a statutory board, Public Utilities Board (PUB), formed for all water-related services.
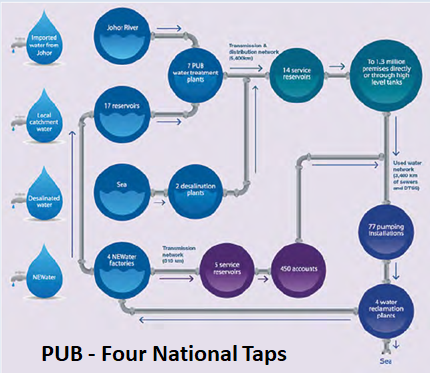
WATER UTILITY REFORMS:
Under this , the two water utilities that have undergone major transformations as a result of undertaking water sector reforms have been selected as case studies. 21
Phnom Perth. Cambodia – Implementing reforms with good governance: This case is an example of how good governance can transform the performance of a public water utility.
Burkina Faso – Corporate approach to operations: A corporatization approach was adopted by the water utility with the help of a performance-based service contract with an international operator and the government’s support through a tariff and investment policy.
In India, most of the public-owned urban water and sanitation utilities are in a dismal state, performing below their potential and resulting in the widening of the gap between demand and supply. In this context, the case of transformation of ONEA in Burkina Faso shows that corporatization of the water utility, i.e., increasing cost recovery and improving the efficiency of service provision have been important elements in the turnaround of the utility. Corporatization, which requires autonomy for a water utility from political interference and operational arrangements like that of a business entity (comprising transparent management, reward for employees to perform, and internal control systems in the form of audits), is a critical element
LOSS PREVENTION AND LEAKAGE CONTROL:
Case studies of methodologies adopted for the prevention of physical as well as commercial loss during water transmission, distribution and metering 21
Tokyo, Japan – Physical loss reduction: The initiative involves adoption of continuous technological improvements for reduction of leakage rate from 20% in 1955 to 2.7% in 2010.
Dublin, Ireland – District Metered Areas (DMAs): The project demonstrates the use of a target-cost contract aimed at reducing leakage over a two-year period from 4.0% to 20% by delineating districts as per the DMA approach.
Sao Paulo, Brazil – Commercial loss reduction: The program is an example of reducing commercial losses by means of a strategy involving replacement of customer meters and the reduction of bad debts.
The water utilities in most Indian cities are faced with similar issues of inefficiency in bill collection and cost recovery mechanisms, which results in revenue losses. The approach adopted in Sao Paulo of contracting for the large meter replacement is similar to a build-operate-transfer (BOT) model under public and private partnerships. This model can be replicated in cities where the utility has a significant number of large customers and a high tariff for the top consumption categories, for it to be cost effective.
Register & Download PDF for Educational Purposes Only
Urban Infrastructure and Network Study notes for M. plan Sem-III

Urban Infrastructures & Network.pdf
Register as member and login to download attachment [pdf] by right-click the pdf link and Select “Save link as” use for Educational Purposes Only
Disclaimer
Information on this site is purely for education purpose. The materials used and displayed on the Sites, including text, photographs, graphics, illustrations and artwork, video, music and sound, and names, logos, IS Codes, are copyrighted items of respective owners. Front Desk is not responsible and liable for information shared above.