- FORUM
- PROJECTS
- ABOUT US
- RESOURCES
- CONTACT US
- FORUM
- PROJECTS
- ABOUT US
- RESOURCES
- CONTACT US
During aerobic composting, microorganisms oxidize organic compounds to carbon dioxide (CO2), nitrite, and nitrate. Carbon from organic compounds is used as a source of energy while nitrogen is recycled. Due to chemical reactions producing heat, temperature of the mass rises.
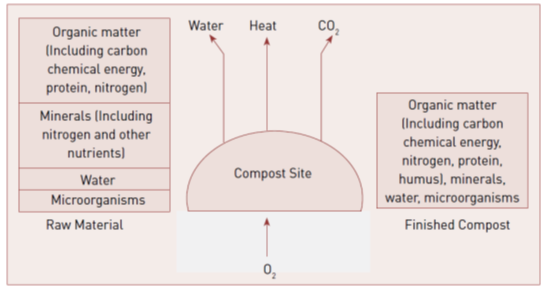
Several biological, chemical, and physical processes contribute to the success of the aerobic composting
Biological process
thermophilic stage (sanitisation)
Mesophilic stage (decomposition).
Curing Stage
Chemical Process
Moisture: moisture content should be high
Aeration: High oxygen levels in air voids
Carbon-to-Nitrogen Ratio of around 30:1,
Physical Process
Temperature : rise beyond 70°C
Particle Size: enough void space to allow air to circulate
Register & Download PDF for Educational Purposes Only
Urban Infrastructure and Network Study notes for M. plan Sem-III

Urban Infrastructures & Network.pdf
Register as member and login to download attachment [pdf] by right-click the pdf link and Select “Save link as” use for Educational Purposes Only
Disclaimer
Information on this site is purely for education purpose. The materials used and displayed on the Sites, including text, photographs, graphics, illustrations and artwork, video, music and sound, and names, logos, IS Codes, are copyrighted items of respective owners. Front Desk is not responsible and liable for information shared above.