- FORUM
- PROJECTS
- ABOUT US
- RESOURCES
- CONTACT US
- FORUM
- PROJECTS
- ABOUT US
- RESOURCES
- CONTACT US
SEWAGE TREATMENT PROCESS Activated Sludge Process (ASP)
• Fixed Bed Biofilm Activated Sludge Process (FBAS)
• Fixed media like Rotating Biological Contactor (RBC)
• Oxidation ditch (O D)
Activated Sludge Process (ASP)
There are two variations of this process namely,
(a) the conventional process for removal of BOD and SS alone and
(b) additionally incorporation of biological nitrification & denitrification for removal of nitrogen in the same process.
Within the conventional process, there are other variations as in Figure 5.6. In the case of very small STPs bleeding excess sludge will be a hydraulic challenge and hence mixed liquor can be wasted intermittently.
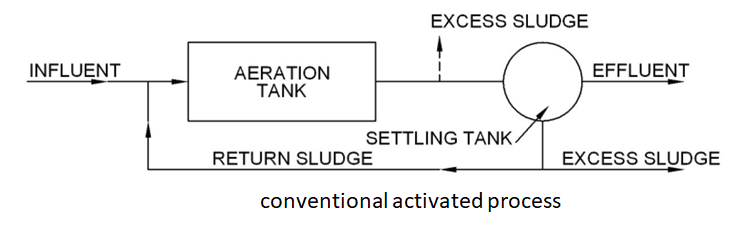
The conventional system represents the early development of the ASP which is more than 100 years old.
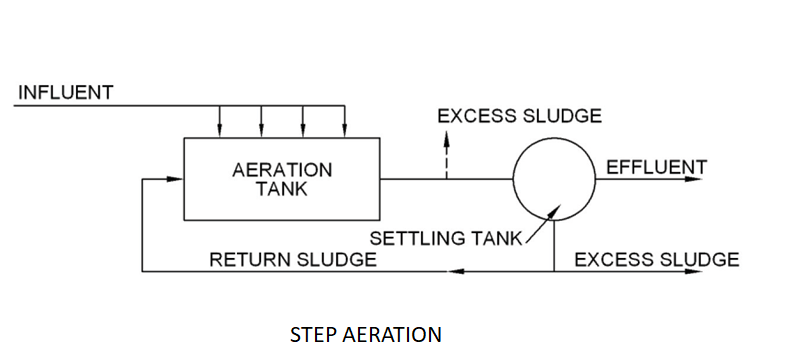
Over the years, several modifications to the conventional system have been developed to meet specific treatment objectives.
In step aeration, settled sewage is introduced at several points along the tank length which produces a uniform oxygen demand throughout.
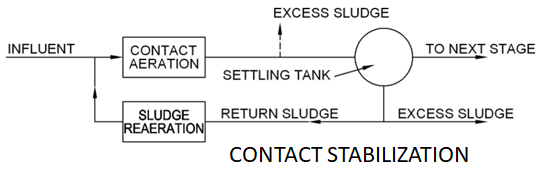
Contact stabilization provides for reaeration of return activated sludge from the final clarifier, which allows a smaller aeration or contact tank.
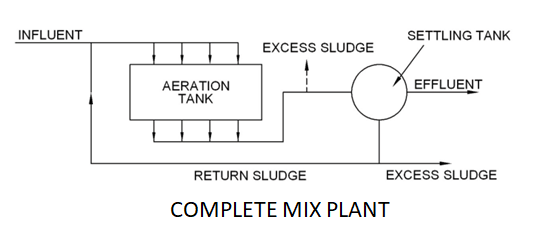
While conventional system maintains a plug flow hydraulic regime, completely mixed process aims at instantaneous mixing of the influent waste and return sludge with the-entire contents of the aeration tank.
Register & Download PDF for Educational Purposes Only
Urban Infrastructure and Network Study notes for M. plan Sem-III

Urban Infrastructures & Network.pdf
Register as member and login to download attachment [pdf] by right-click the pdf link and Select “Save link as” use for Educational Purposes Only
Disclaimer
Information on this site is purely for education purpose. The materials used and displayed on the Sites, including text, photographs, graphics, illustrations and artwork, video, music and sound, and names, logos, IS Codes, are copyrighted items of respective owners. Front Desk is not responsible and liable for information shared above.