- FORUM
- PROJECTS
- ABOUT US
- RESOURCES
- CONTACT US
- FORUM
- PROJECTS
- ABOUT US
- RESOURCES
- CONTACT US
Damp and Water Insulation Materials
Types of DampnessBased on the movement of moisture the dampness can be of the following three types:
- Rising or capillary dampness.
- Falling or penetrating dampness.
- Condensation dampness.
Some Definitions
Peeling off
This term is related to plaster and it means that the plaster surface get disfigured.
BlisteredThese term are related to Painting.
DPC (Damp proof course)It is a continuous layer of impervious material between source of dampness and building component.
Causes of Dampness.
Following are the main causes of dampness in a building
- Rain penetration
It is the main source of dampness. Heavy rain of short duration is less dangerous. rain water enters through joints, cracks and porous bricks or stones.
- Level of site
Low laying building sites are effected by the depositing surface water and underground water.
- Drainability of the Soil
Course grained soils like Sandy or gravely soils provides good drainibility conditions and fine grained soils like clay retain water and cause dampness.
- Climatic conditions
In cold climatic condition dampness causes due to condensation of water vapors.
- Defective Orientation
If building is exposed to direct rain showers and less sun rays then it cause dampness.
- Entraped moisture in the building
Due Over soaked bricks and use of salty or alkaline water results dampness in building.
- Defective construction material
Porous bricks, soft stones, alkaline water etc. cause dampness of building.
- Defective construstion
Through defective joints of parapet, copping and masonry joints moisture can enter in the building.
- Moisture originates in the building.
It is due to the leakage through water supply or sanitary system of building.
Effects of Dampness
Following are the harmful effects of dampness in buildings:
- Building become esthetically poor.
- It cause dry Rot to the wooden members provided in the building.
- It cause corrosion of metals used in building.
- Plaster peels off.
- Paint blistered and bleached and the surface disfigured.
- Holes and pits are formed in topping of floors.
- Efflorescence occurs and bricks disintegrate and turn in to powder.
- Un hygienic conditions in building.
Remedial Measures
- By Damp Proofing Courses (DPC)
- By surface treatment
- By water proofing construction
- By special devices/techniques
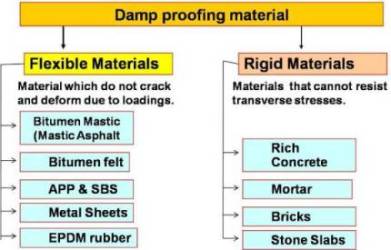
Damp proofing material
- Classification of Damp proofing material
- Qualities of a good Damp proofing Material
- Important places for Damp proofing materials.
Classification of Damp proofing material
Asphalt, Bitumen And Tar
- Asphalt, bitumen and tar are hydrocarbons.
- Asphalt and bitumen are petroleum products
- Tar is a dark coloured product obtained from destructive distillation of organic substances like coal, wood or bituminous shales.
- Asphalt also appears in nature as natural deposits.
Mastic Asphalt
Asphalt: A mixture of bitumen and mineral filler. Note that Hot Rolled Asphalt is a road surfacing material.
Mastic: An adhering asphalt which is placed with trowelling.
Mastic asphalt is a type of asphalt usually around 7–10% of the whole aggregate mix, This thermoplastic substance and used in waterproofing flat roofs and tanking underground. Mastic asphalt is heated to a temperature of 210 °C (410 °F) and is spread in layers to form an impervious barrier about 20 millimeters (0.79 in) thick.
Applied in hot state in 1” to 2” (2 cm to 5 cm)

Bitumen felt ( plastomeric system).IS Code of Practice 1346
Many Type of Bituminuous sheet are used for water proofing works mainly two type of plastic based bitumen sheet are available :
Traditional felt : Which is to be stuck to the surface to be waterproofed with hot blown asphalt
Thermofusible film : sheet with underside of thermofusible film which can be heated by gas flame torch and then stick to the hot surface.
Major disadvantage : most of these membranes last only five to six years and we have to remove old and reinstall new system
- MARKET PRODUCT :
- UNIFELT : bituminous felt
- UNIPLASTIFELT : It consists of a centre core of 25 microns thick high molecular high density polythyene film.
By UNITED TAR (P) LTD. - 6 mm thick bitumen sheet available in roll form
Modified Bitumen
modified bitumen= bitumen + plastic There are two types :
- APP ( Atactic Poly Propylene ) plastomer
- SBS ( Sequenced Butadiene Styrene) elastomer
APP modified bitumen is generally stronger and stiffer the SBS modified bitumen , which has greater flow for expansion and waterproofing qualities
Both have high tolerance for UV rays
Its preferred over hot mastic asphalt / bitumen
- MARKET PRODUCT :
- NILOBIT-PM & NILOBIT-PN are Polyester Reinforced Membrane
- NILOBIT-FN is Fibreglass Reinforced Membrane.
- By UNITED TAR (P) LTD.

Thickness: 2mm,3mm,4mm
Lead, copper, Aluminum sheets
Insulation sheet with Aluminum
- water,sound and fire proof
- closed-cell flexible
- Low thermal conductivity
aluminum flex sheet and roll insulation is a flexible, elastomeric thermal insulation, black in color. It is furnished with a smooth skin on one side which forms the outer exposed insulation surface. Lead can react chemically with cement
Lead should be laid in lime mortar. Minimum thickness of copper sheets should be 3 mm

EPDM rubber
Ethylene Propylene Diene Monomer is a synthetic rubber most commonly used in single-ply roofing because it is readily available and relatively simple to apply. EPDM as a roofing membrane has advanced significantly over recent years. Problems previously associated with it included moisture gain under the membrane by vapour drive (occurring on roofs with air conditioned space beneath), and that EPDM did not like to adhere to itself and seam problems occurred. Simply adding a vapour barrier will help to resolve vapour drive.
- MARKET PRODUCT :
- STARSEAL 100 by STAR COATING & MEMBRANES PVT. LTD.
- POLY FLEX by M/s. POLY RUBBER PRODUCTS

Rigid Materials
Rich Concrete
1” to 2-1/2” thick layer of P.C.C (1:2:4) painted with hot bitumen is applied
MortarRich or fat cement mortar (1:3) is laid in ¾” thickness (2 cm) as vertical DPC.
Painted with bitumen
BricksOver burnt bricks are used in two layers in (1:3) mortar
Stone SlabsTwo layers of stone slabs in lime cement and sand mortar (1:1:6) is provided in areas where stone is easily available.
Qualities of a good Damp proofing Material
- Impervious
- Durable
- Non disintegratable
- Stable under the loading
- Level finish
- Full coverage of wall thickness
- Availability
- Economical
Important places for Damp proofing materials
- At Plinth Level (in walls ) (external & Internal)
- Parapet walls
- Window sill
- Basements and Under ground Floors
Information on this site is purely for education purpose. The materials used and displayed on the Sites, including text, photographs, graphics, illustrations and artwork, video, music and sound, and names, logos, IS Codes, are copyrighted items of respective owners. They are provided here just for refrence/information.
For your views and discussions Register in FDAchitects Forum …