- FORUM
- PROJECTS
- ABOUT US
- RESOURCES
- CONTACT US
- FORUM
- PROJECTS
- ABOUT US
- RESOURCES
- CONTACT US
Tools used in Project monitoring include
1. Project Management Software: Software that provides tools for scheduling, budgeting, and tracking project progress. There are many project management software available in the market, some of the most popular ones are:
1.1 Oracle Primavera P6 EPPM is a project, program and portfolio management tool that is used for planning, managing and executing your project work.
1.2 Asana: A cloud-based project management tool that provides a comprehensive platform for tracking tasks, projects, and teams.
1.3 Trello: A visual project management tool that uses a kanban board-style interface to help teams organize and prioritize their work.
1.4 Monday.com: A cloud-based project management tool that offers a wide range of features for managing projects, including task management, resource management, and real-time collaboration.
1.5 Jira: A popular project management tool used by software development teams to track and manage software development projects.
1.6 Basecamp: A web-based project management tool that provides a centralized platform for managing projects, tasks, and team communication.
1.7 Microsoft Project: A project management tool from Microsoft that provides a comprehensive platform for project planning, tracking, and reporting.
1.8 Smartsheet: A cloud-based project management tool that offers a wide range of features for managing projects, including task management, resource management, and Gantt chart views.
2. Gantt Charts: A graphical representation of the project schedule that displays the start and end dates of tasks and their dependencies.
Gantt charts are a commonly used tool in project monitoring, as they provide a visual representation of the project schedule. A Gantt chart displays the start and end dates of tasks and their dependencies, making it easier to see the inter-relationships between tasks and to monitor the progress of the project.
Some of the key benefits of using Gantt charts in project monitoring are:
2.1 Schedule Overview: Gantt charts provide a high-level overview of the project schedule, making it easier to understand the project’s timeline and to identify potential schedule conflicts.
2.2 Progress Tracking: Gantt charts allow project managers to see the status of tasks, including completed tasks, ongoing tasks, and tasks that are behind schedule.
2.3 Resource Allocation: Gantt charts help project managers to see the allocation of resources, such as manpower and equipment, and to assess the impact of resource constraints on the project schedule.
2.4 Dependency Tracking: Gantt charts help project managers to track the inter-relationships between tasks and to understand how changes to one task may impact other tasks in the project.
2.6 Communication Tool: Gantt charts can be used as a communication tool between project team members, stakeholders, and clients, providing a clear and concise overview of the project’s progress and status.
3.0 Earned Value Analysis(EVA) : A technique used to monitor project performance by comparing the actual progress of the project to the planned progress.
EVA combines information on the planned cost, actual cost, and the progress of work completed to calculate various performance measures, such as the Cost Performance Index (CPI), Schedule Performance Index (SPI), and the Estimate at Completion (EAC). Some of the benefits of using EVA in urban infrastructure project monitoring are:
3.1 Budget Monitoring: EVA helps project managers to monitor the project’s budget and to identify potential budget overruns at an early stage.
3.2 Schedule Monitoring: EVA helps project managers to assess the project’s progress against the schedule and to identify potential schedule delays.
3.3 Resource Utilization: EVA provides information on the utilization of resources, such as manpower, equipment, and materials, helping project managers to assess the impact of resource constraints on the project.
3.4 Forecasting: EVA can be used to forecast the final cost of the project and the completion date, based on the progress to date and the remaining work to be done.
3.5 Decision Making: EVA provides project managers with data-driven insights that can be used to make informed decisions on project planning, risk management, and resource allocation.
4. Quality Control Inspections: Inspections performed at various stages of the project to verify that the work meets the specified quality standards.
The purpose of quality control inspections is to ensure that the project is constructed according to the specified standards and requirements, and to identify and rectify any defects or non-conformances. Some of the key benefits of quality control inspections in urban infrastructure project monitoring are:
4.1 Compliance: Quality control inspections help to ensure that the project is being constructed in compliance with the relevant regulations, codes, and standards.
4.2 Defect Identification: Quality control inspections help to identify any defects or non-conformances in the construction work, allowing project managers to take corrective action to rectify them.
4.3 Continuous Improvement: Quality control inspections provide valuable feedback on the quality of the construction work, helping project managers to identify areas for improvement and to implement continuous improvement processes.
4.4 Cost Savings: By identifying and rectifying defects and non-conformances at an early stage, quality control inspections can help to reduce the costs associated with rework, warranty claims, and litigation.
4.5 Stakeholder Confidence: Quality control inspections help to build confidence among stakeholders in the project, as they demonstrate the commitment to delivering a high-quality project.
Quality control inspections are typically carried out by a dedicated team of quality control inspectors who have the technical knowledge and expertise to assess the construction work against the specified standards and requirements. These inspections can be scheduled at regular intervals or carried out on an ad-hoc basis, depending on the specific needs of the project.
5. Risk Registers: A document that lists potential risks and the actions that can be taken to mitigate them.
Risk registers help project managers to identify, assess, and manage risks throughout the project lifecycle. A risk register is a document that lists the potential risks associated with a project, along with information on the likelihood of each risk occurring and the potential impact of the risk on the project. Some of the key benefits of using risk registers in urban infrastructure project monitoring are:
5.1 Risk Awareness: Risk registers help project managers to become aware of the potential risks associated with a project, allowing them to take proactive measures to mitigate or avoid those risks.
5.2 Risk Assessment: Risk registers provide a structured approach to risk assessment, helping project managers to assess the likelihood and impact of each risk and to prioritize risks based on their severity.
5.3 Risk Management: Risk registers help project managers to develop and implement risk management strategies to mitigate or avoid risks, and to monitor the effectiveness of those strategies.
5.4 Stakeholder Communication: Risk registers can be used to communicate the risks associated with the project to stakeholders, helping to build transparency and trust in the project.
5.5 Continuous Improvement: Risk registers can be updated throughout the project lifecycle, helping project managers to continuously monitor and assess the risk profile of the project, and to make changes to risk management strategies as necessary.
5.6 Risk registers help project managers to identify and manage risks, and to ensure the successful completion of the project. By using risk registers, project managers can proactively manage risks, reducing the likelihood of project delays, budget overruns, and other risks that can negatively impact the project.
6. Status Reports: Regular reports that provide an update on the progress of the project and any issues or risks that have arisen.
Status reports provide regular updates on the progress, performance, and status of the project. Status reports typically include information on the project schedule, budget, risks, and quality, along with any other relevant information that is relevant to the project. Some of the key benefits of using status reports in urban infrastructure project monitoring are:
6.1 Project Progress: Status reports provide a clear view of the project’s progress, allowing project managers to assess the project’s performance and to identify any potential issues or risks.
6.2 Budget Monitoring: Status reports help project managers to monitor the project’s budget, and to identify any potential budget overruns or savings.
6.3 Schedule Monitoring: Status reports help project managers to assess the project’s progress against the schedule, and to identify any potential schedule delays.
6.4 Risk Management: Status reports provide information on the status of risks, including the likelihood and impact of each risk, and the risk management strategies that have been implemented.
6.5 Stakeholder Communication: Status reports are an effective way to communicate the progress, performance, and status of the project to stakeholders, including project team members, sponsors, and customers.
Status reports can be produced on a regular basis, such as weekly, monthly, or quarterly, depending on the specific needs of the project. They can be produced in a variety of formats, including written reports, presentations, or interactive dashboards.
for more detail download
 Professional Practice unit 5.pdf
Professional Practice unit 5.pdf
FD Planning Community Forum Discussion
- Community Participation Process in planning
- Appreciation of decision-making processes
- Process in relation to varied consultancy assignments of planning
- Project Financing Need Assessment
- Projects Financing : Sources of funds
- The disposition of funds in urban development projects
- Planning for project Financing
- Project Monitoring and Criteria for decision making
- Project monitoring : Parameters and Tools of Control
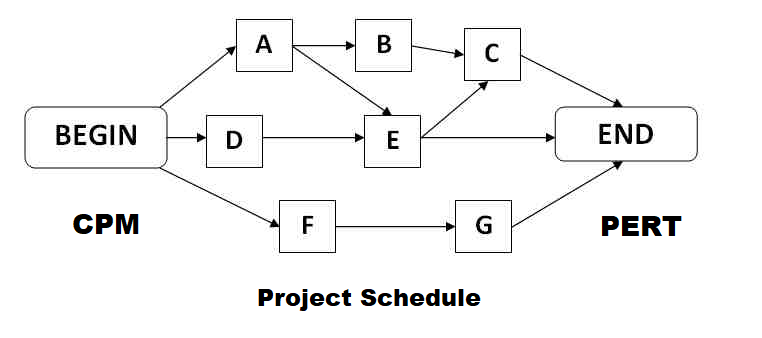
- Use of Network Analysis in Project Monitoring
- Reporting and Corrective Actions
- Resource management and project reporting
- Project Evaluation- Methods, tools, time frame and results
- Project Cash Flows
- Principles of Cash Flow Estimation
- Project Benefits
- Financial closure of project
- Presentation of evaluation findings
Disclaimer
Information on this site is purely for education purpose. The materials used and displayed on the Sites, including text, photographs, graphics, illustrations and artwork, video, music and sound, and names, logos, IS Codes, are copyrighted items of respective owners. Front Desk is not responsible and liable for information shared above.