- FORUM
- PROJECTS
- ABOUT US
- RESOURCES
- CONTACT US
- FORUM
- PROJECTS
- ABOUT US
- RESOURCES
- CONTACT US
Daylight factor is the sum of all the daylight reaching on an indoor reference point from the following sources:
1.Direct sky visible from the point, expressed as the sky component (SC),
2.External surfaces reflecting light directly to the point , expressed as the externally reflected component (ERC),
3.Internal surfaces reflecting and inter-reflecting light to the point, expressed as the internally reflected component (IRC).
DF = SC+ ERC+IRC
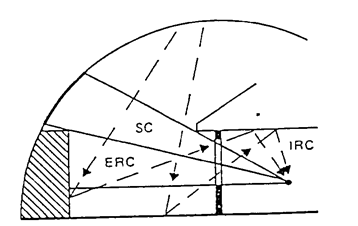
Design variable for SC
- Area of sky visible from point
- Average altitude angle
- Window size
- Window position in relation to point
- Thickness of window frame member
- Quality of glass
- External obstruction
Design variable for ERC
- The Area of external surface visible from the point
- Reflectance of external surface
Design variable for IRC
- Size of Room
- The ratio of wall etc.
- Surface in relation to window area
- Reflectance of indoor surfaces
Sky component (SC)
The sky component of Daylight Factor (DF) refers to the contribution of the light from the sky to the total amount of natural light that enters a space. The sky component of DF is a measure of the amount of light that is transmitted through the sky and into a space, and it is influenced by several factors, including the position of the sun, the time of day, and the weather conditions.
The sky component of DF can be calculated using mathematical models that take into account the position of the sun, the geometry of the building, and the optical properties of the surrounding environment. These models are typically based on the principles of radiative transfer and use sky luminance distributions to calculate the amount of light that is transmitted through the sky and into a space.
The sky component of DF is an important consideration in daylighting design, as it can provide information about the amount of natural light that is likely to be available in a space under different sky conditions. By designing lighting systems that take into account the sky component of DF, lighting professionals can optimize the use of natural light and create sustainable and energy-efficient buildings that promote occupant health and well-being.
Externally reflected component (ERC)
The externally reflected component of Daylight Factor (DF) refers to the contribution of the light that is reflected off external surfaces, such as adjacent buildings or the ground, to the total amount of natural light that enters a space. The externally reflected component of DF is a measure of the amount of light that is reflected off external surfaces and into a space, and it is influenced by several factors, including the reflectivity of surrounding surfaces and the geometry of the surrounding environment.
The externally reflected component of DF can be calculated using mathematical models that take into account the optical properties of the surrounding environment and the geometry of the building. These models typically use radiative transfer principles to calculate the amount of light that is reflected off external surfaces and into a space.
The externally reflected component of DF is an important consideration in daylighting design, as it can provide information about the amount of natural light that is likely to be available in a space under different external surface conditions. By designing lighting systems that take into account the externally reflected component of DF, lighting professionals can optimize the use of natural light and create sustainable and energy-efficient buildings that promote occupant health and well-being.
Internally reflected component (IRC)
The internally reflected component (IRC) of Daylight Factor (DF) refers to the contribution of the light that is reflected off internal surfaces within a space, such as walls, floors, and ceilings, to the total amount of natural light that enters the space. The IRC of DF is a measure of the amount of light that is reflected off internal surfaces and redistributed within a space, and it is influenced by several factors, including the reflectivity of the internal surfaces, the geometry of the space, and the position of the openings.
The IRC of DF can be calculated using mathematical models that take into account the optical properties of the internal surfaces, the geometry of the space, and the position and size of the openings. These models typically use radiative transfer principles to calculate the amount of light that is reflected off internal surfaces and redistributed within the space.
The IRC of DF is an important consideration in daylighting design, as it can provide information about the amount of natural light that is likely to be available within a space due to internal reflections. By designing lighting systems that take into account the IRC of DF, lighting professionals can optimize the use of natural light and create sustainable and energy-efficient buildings that promote occupant health and well-being.
Daylight Factor (DF) is a measure of the amount of natural light that enters a space relative to the amount of available natural light outside. It is an important consideration in daylighting design, as it can provide information about the amount of natural light that is likely to be available in a space and can help lighting professionals to create sustainable and energy-efficient buildings that promote occupant health and well-being.
Illumination in architecture – home page
FD Architect Community Forum Discussion
- Illumination – introduction
- Basic Terminology and Definitions
- Laws of Illumination The Inverse Square Law of Illuminance Illuminance (E) at any poi
- Laws of Reflection and Refraction
- Visual efficiency & comfort
- Day lighting
- Components of Daylight Factor
- Artificial Lighting Design
Download Study Notes PDF
Register as member and login to download attachment use this only for Educational Purpose
Disclaimer
Information on this site is purely for education purpose. The materials used and displayed on the Sites, including text, photographs, graphics, illustrations and artwork, video, music and sound, and names, logos, IS Codes, are copyrighted items of respective owners. Front Desk is not responsible and liable for information shared above.
1 Comment
[…] Components of Daylight Factor […]