- FORUM
- PROJECTS
- ABOUT US
- RESOURCES
- CONTACT US
- FORUM
- PROJECTS
- ABOUT US
- RESOURCES
- CONTACT US
The primary source of lighting for daylighting is the sun.
In daylighting design, the goal is to maximize the use of natural light while minimizing the negative effects of glare and heat gain. This can be achieved through a range of strategies, including the use of daylight-responsive controls, such as automated shading systems and sensors that adjust electric lighting in response to changes in natural light levels.
The light received by the earth from the sun consists of two parts, namely, direct solar illuminance and sky illuminance
Sky illuminance is influenced by a range of factors, including the time of day, weather conditions, and the orientation and location of the building. In general, the amount of sky illuminance that is available is highest at midday on a clear day, and decreases as the sun moves closer to the horizon or as cloud cover increases.
In daylighting design, sky illuminance is often measured in units of lux, which indicate the amount of light that is received per unit of area. Sky illuminance can be predicted using computer simulations and models that take into account a range of variables, including the orientation and location of the building, the size and placement of windows, and the reflectivity of surrounding surfaces.
By carefully considering the amount of sky illuminance that is available in a space, lighting professionals can design lighting systems that maximize the use of natural light and minimize the need for electric lighting. This can help to reduce energy consumption and improve overall occupant comfort and well-being.
For the purposes of daylighting design, direct solar illuminance shall not be considered and only sky illuminance shall be taken as contributing to illumination of the building interiors during the day.
Daylight factor (DF)
Daylight factor (DF) is the ratio of the light level inside a structure to the light level outside the structure.
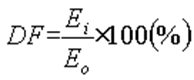
Ei = illumiance due to daylight at a point on the indoors working plane
Eo = simultaneous outdoor illuminance on a horizontal plane from an unobstructed hemisphere of overcast sky
Daylight Factor (DF) is a measure of the amount of natural light that enters a space relative to the amount of available natural light outside. It is expressed as a percentage and is calculated by dividing the illuminance (in lux) inside a room by the illuminance (in lux) that would exist at a point immediately outside the window.
DF is an important consideration in daylighting design, as it can provide information about the amount of natural light that is likely to be available in a space at different times of the day and under different weather conditions. A higher DF indicates that more natural light is entering the space, while a lower DF indicates that less natural light is entering the space.
DF can be influenced by a range of factors, including the size and orientation of the window, the reflectivity of surrounding surfaces, and the presence of shading devices such as overhangs or blinds. In general, a higher DF is desirable in spaces where visual tasks are performed, such as offices, classrooms, and libraries.
DF can be calculated using computer simulations and models that take into account a range of variables, including the location and orientation of the building, the size and placement of windows, and the reflectivity of surrounding surfaces. By carefully designing lighting systems that take into account the DF of a space, lighting professionals can create sustainable and energy-efficient buildings that promote occupant health and well-being.
Daylight Factor (DF) is a measure of the amount of natural light that enters a space relative to the amount of available natural light outside. It is an important consideration in daylighting design, as it can provide information about the amount of natural light that is likely to be available in a space and can help lighting professionals to create sustainable and energy-efficient buildings that promote occupant health and well-being.
Illumination in architecture – home page
FD Architect Community Forum Discussion
- Illumination – introduction
- Basic Terminology and Definitions
- Laws of Illumination The Inverse Square Law of Illuminance Illuminance (E) at any poi
- Laws of Reflection and Refraction
- Visual efficiency & comfort
- Day lighting
- Components of Daylight Factor
- Artificial Lighting Design
Download Study Notes PDF
Register as member and login to download attachment use this only for Educational Purpose
Disclaimer
Information on this site is purely for education purpose. The materials used and displayed on the Sites, including text, photographs, graphics, illustrations and artwork, video, music and sound, and names, logos, IS Codes, are copyrighted items of respective owners. Front Desk is not responsible and liable for information shared above.
2 Comments
[…] Day lighting […]
[…] Day lighting […]