- FORUM
- PROJECTS
- ABOUT US
- RESOURCES
- CONTACT US
- FORUM
- PROJECTS
- ABOUT US
- RESOURCES
- CONTACT US
Project evaluation
Project evaluation is the process of assessing the performance and effectiveness of a project, typically after its completion. Project evaluation is an important tool for ensuring that the project has achieved its objectives and for improving future projects.
1. Methods
The following are some common methods of project evaluation:
1.1 Outcome evaluation: This involves assessing the results or outcomes of the project, such as the level of achievement of project objectives, the impact of the project on target beneficiaries, and the sustainability of the project results.
1.2 Impact evaluation: This involves assessing the long-term effects of the project, such as changes in attitudes, behaviors, or conditions.
1.3 Process evaluation: This involves assessing the performance of the project team, the effectiveness of the project management processes, and the quality of project outputs.
1.4 Cost-Benefit Analysis: This involves assessing the economic value of the project by comparing the costs incurred to the benefits generated by the project.
1.5 Performance evaluation: This involves assessing the efficiency and effectiveness of the project in terms of meeting project objectives, using resources, and delivering outcomes.
1.6 Stakeholder analysis: This involves assessing the perspectives and opinions of stakeholders, such as project beneficiaries, project partners, and funding organizations, regarding the project’s performance and impact.
1.7 Lessons Learned: This involves identifying the lessons learned from the project, including what worked well and what could be improved in future projects.
Project evaluation is a valuable tool for ensuring that projects are managed effectively, for improving future projects, and for demonstrating accountability to stakeholders. By regularly evaluating projects, project managers can make informed decisions, allocate resources more effectively, and improve the chances of project success.
2. Tools
The following are some common tools used for project evaluation:
2.1 Surveys: Surveys can be used to gather feedback from project stakeholders, including beneficiaries, partners, and funding organizations. This feedback can provide valuable insight into the effectiveness of the project and the impact it has had.
2.2 Key Performance Indicators (KPIs): KPIs are measurable values that provide insight into the performance of the project. KPIs can include metrics such as project completion rate, budget adherence, and resource utilization.
2.3 Benchmarking: Benchmarking involves comparing the performance of the project to that of similar projects, or to established industry standards. This can help to identify best practices and areas for improvement.
2.4 Root Cause Analysis: Root cause analysis is a process used to identify the underlying causes of problems in the project. This can help to identify areas for improvement and to develop corrective actions to prevent similar issues from occurring in future projects.
2.5 Cost-Benefit Analysis: Cost-benefit analysis is a tool used to evaluate the economic value of a project by comparing the costs incurred to the benefits generated by the project.
2.6 Performance Audits: Performance audits are independent assessments of the performance of the project, typically conducted by external experts. Performance audits can provide valuable insights into the performance of the project and help to identify areas for improvement.
2.7 Stakeholder Feedback: Feedback from stakeholders can provide valuable insights into the performance and impact of the project. This feedback can be gathered through surveys, interviews, or focus groups.
By using these tools, organizations can effectively evaluate the performance and impact of their projects, and make improvements to ensure that future projects are managed more effectively
3. Time Frame
The time frame for project evaluation depends on the nature and scope of the project, as well as the objectives of the evaluation. Project evaluations can be conducted at various stages of a project, including during the planning phase, during implementation, and after completion.
3.1 Mid-term evaluation: A mid-term evaluation is usually conducted halfway through the project and can help to assess the progress of the project and identify any issues that need to be addressed.
3.2 Final evaluation: A final evaluation is typically conducted after the project has been completed. This type of evaluation provides an opportunity to assess the overall performance of the project, including the achievement of project objectives and the impact of the project.
3.3 Continuous evaluation: Continuous evaluation is an ongoing process that involves regular monitoring and assessment of the project as it progresses. This can help to identify issues early and to make adjustments to the project as needed.
The frequency and timing of project evaluations will depend on the objectives of the evaluation and the resources available for the evaluation. It is important to plan the evaluation process carefully, taking into account the specific needs of the project and the stakeholders involved.
4. Results
The results of a project evaluation can have significant implications for the future of the project, as well as for the organization responsible for the project. The results of a project evaluation can be used to:
4.1 Assess performance: The results of a project evaluation can provide valuable insights into the performance of the project, including the achievement of project objectives and the effectiveness of project management.
4.2 Identify areas for improvement: The results of a project evaluation can help to identify areas for improvement, both in terms of project management and in terms of the impact of the project.
4.3 Inform future projects: The results of a project evaluation can inform future projects, by providing valuable lessons learned and best practices that can be applied to future projects.
4.4 Enhance reputation: A well-conducted project evaluation can enhance the reputation of the organization responsible for the project, demonstrating its commitment to transparency, accountability, and continuous improvement.
4.5 Foster stakeholder engagement: The results of a project evaluation can be used to engage stakeholders, including beneficiaries, partners, and funding organizations, and to build trust in the organization and its projects.
4.6 Secure funding: The results of a project evaluation can be used to secure additional funding for the project or for future projects, by demonstrating the value and impact of the project.
4.7 Improve decision making: The results of a project evaluation can inform decision making, by providing valuable data and insights that can be used to make informed decisions about the future of the project and the organization.
It is important to effectively communicate the results of a project evaluation, both within the organization and to external stakeholders, in order to maximize the benefits of the evaluation process.
for more detail download
![[Image: pdf.gif]](https://frontdesk.co.in/forum/images/attachtypes/pdf.gif) Professional Practice unit 5.pdf
Professional Practice unit 5.pdf
FD Planning Community Forum Discussion
- Community Participation Process in planning
- Appreciation of decision-making processes
- Process in relation to varied consultancy assignments of planning
- Project Financing Need Assessment
- Projects Financing : Sources of funds
- The disposition of funds in urban development projects
- Planning for project Financing
- Project Monitoring and Criteria for decision making
- Project monitoring : Parameters and Tools of Control
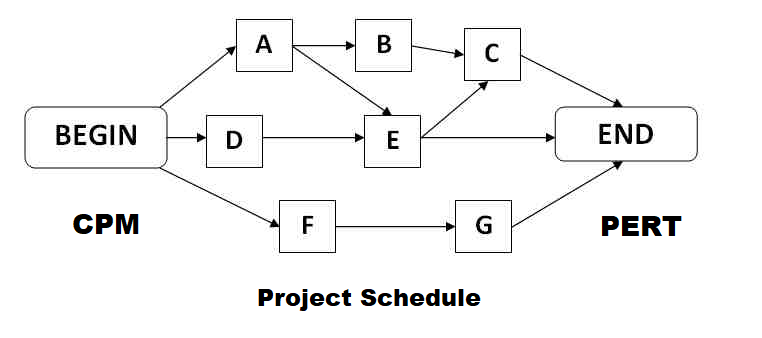
- Use of Network Analysis in Project Monitoring
- Reporting and Corrective Actions
- Resource management and project reporting
- Project Evaluation- Methods, tools, time frame and results
- Project Cash Flows
- Principles of Cash Flow Estimation
- Project Benefits
- Financial closure of project
- Presentation of evaluation findings
Disclaimer
Information on this site is purely for education purpose. The materials used and displayed on the Sites, including text, photographs, graphics, illustrations and artwork, video, music and sound, and names, logos, IS Codes, are copyrighted items of respective owners. Front Desk is not responsible and liable for information shared above.