- FORUM
- PROJECTS
- ABOUT US
- RESOURCES
- CONTACT US
- FORUM
- PROJECTS
- ABOUT US
- RESOURCES
- CONTACT US
Ditch and Furrow Method:
In areas with irregular topography, shallow, flat bottomed and closely spaced ditches or furrows provide maximum water contact area for recharge water from source stream or canal. This technique requires less soil preparation than the recharge basins and is less sensitive to silting.
Generally three patterns of ditch and furrow system are adopted 11 1.Lateral Ditch Pattern
2.Dendritic Pattern
3.Contour Pattern
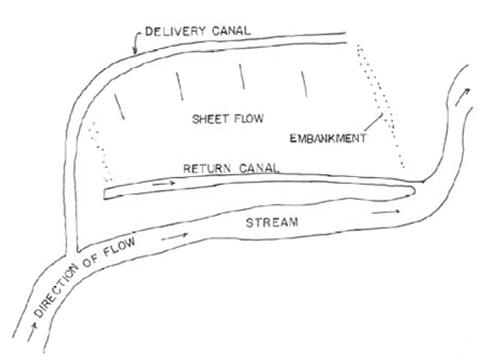
Figure shows a typical plan or series of ditches originating from a supply ditch and trending down the topographic slope towards the stream.
Contour Bunds
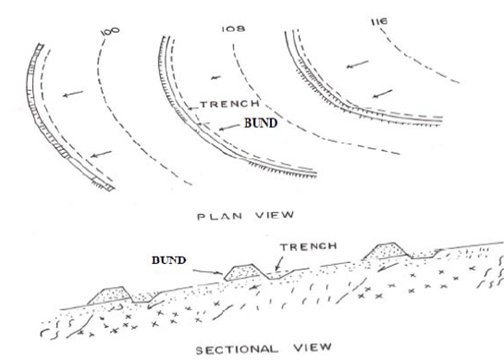
Contour bunding, which is a watershed management practice aimed at building up soil moisture storage involve construction of small embankments or bunds across the slope of the land. They derive their names from the construction of bunds along contours of equal land elevation. This technique is generally adopted in low rainfall areas (normally less than 800 mm) where gently sloping agricultural lands with very long slope lengths are available and the soils are permeable.
They are not recommended for soils with poor internal drainage e.g. clayey soils. Schematic of a typical system of contour bunds is shown in Figure
Contour bunding involves construction of narrow-based trapezoidal embankments (bunds) along contours to impound water behind them, which infiltrates into the soil and ultimately augment ground water recharge.
Recharge Pits and Shafts
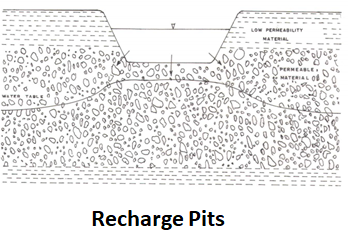
Recharge pits and shafts are artificial recharge structures commonly used for recharging shallow phreatic aquifers, which are not in hydraulic connection with surface water due to the presence of impermeable layers. They do not necessarily penetrate or reach the unconfined aquifers like gravity head recharge wells and the recharging water has to infiltrate through the vadose zone (unsaturated zone). 11
Recharge Pits: Recharge pits are normally excavated pits, which are sufficiently deep to penetrate the low-permeability layers overlying the unconfined aquifers.
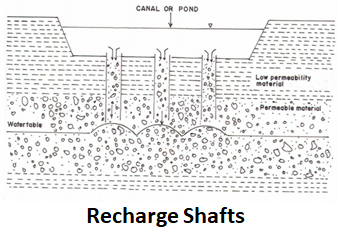
Recharge Shafts are similar to recharge pits but are constructed to augment recharge into phreatic aquifers where water levels are much deeper and the aquifer zones are overlain by strata having low permeability.
Register & Download PDF for Educational Purposes Only
Urban Infrastructure and Network Study notes for M. plan Sem-III

Urban Infrastructures & Network.pdf
Register as member and login to download attachment [pdf] by right-click the pdf link and Select “Save link as” use for Educational Purposes Only
Disclaimer
Information on this site is purely for education purpose. The materials used and displayed on the Sites, including text, photographs, graphics, illustrations and artwork, video, music and sound, and names, logos, IS Codes, are copyrighted items of respective owners. Front Desk is not responsible and liable for information shared above.