- FORUM
- PROJECTS
- ABOUT US
- RESOURCES
- CONTACT US
- FORUM
- PROJECTS
- ABOUT US
- RESOURCES
- CONTACT US
Mobility and accessibility are two key concepts in transportation planning that are often used to describe the quality and availability of transportation options for residents. Mobility and accessibility are the two fundamental benefits transportation is meant to achieve. Let us look at these related, but slightly different benefits.
Mobility is defined as the ability to travel
Accessibility is defined as the ability to reach desired destinations or activities
• Accessibility can be considered to be a combination of mobility and land use patterns.
• Mobility is improved by making travel faster, cheaper, and more convenient.
• Accessibility can be improved in two ways:
1. Transportation investments that improve mobility, and/or
2. More compact land use patterns that locate origins and destinations closer together.

Accessibility is the more important benefit. We travel not for its own sake, but to engage in activities, such as employment and education. This is the reason that accessibility is more important than mobility.
Accessibility is the link between transportation and land use
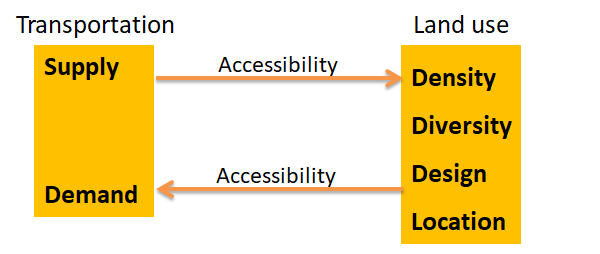
Accessibility is the two-way link between transportation and land use.
Mobility refers to the ease and speed with which people can move within a given area. This includes the availability and quality of different transportation modes, such as public transportation, walking, cycling, and driving. A transportation system that provides high levels of mobility can help to reduce travel times, improve access to employment and essential services, and promote economic growth.
Accessibility, on the other hand, refers to the ease with which people can reach destinations within a given area. This includes the proximity of different transportation modes, the availability of different routes and modes of transportation, and the affordability and convenience of different options. A transportation system that provides high levels of accessibility can help to ensure that all residents can reach essential services and activities, regardless of their income, age, or ability.
Effective transportation planning requires a balance between mobility and accessibility, as both are important for promoting sustainable and equitable growth. This may involve investing in public transportation infrastructure, promoting active transportation modes such as walking and cycling, and adopting policies to reduce reliance on single-occupancy vehicles.
For example, transportation planners may focus on improving the quality and availability of public transportation options to increase mobility for residents who do not have access to private vehicles. At the same time, they may work to promote the development of walkable and bikeable neighborhoods, as well as the construction of safe and accessible infrastructure for pedestrians and cyclists, to improve accessibility and reduce reliance on cars.
The transportation system, or supply, makes some areas more accessible than others which affects how people choose to locate their homes and businesses. This is referred to as land use patterns.
Land use patterns make some areas more attractive as activity centers than others. This affects transportation demand in terms of how many people want to travel to specific locations and which travel modes (e.g., bus, two-wheeler, auto, walking) they choose.
Benefits of land use transport Integration
Land use and Transport Planning home page
Download Study Notes PDF
Land use and Transport Planning.pdf
Register as member and login to download attachment use this only for Educational Purpose
FD Planning Community Forum Discussion
- Land Use Transport Integration and Density of Urban Growth Toolkit
- Integration of Land Use and Transport Planning
- Introduction – Modelling Transport – Ortuzar Willumsen
- Mathematical Prerequisites from Modelling Transport
- data and space from Modelling Transport
- Trip Generation Modelling from Modelling Transport
- Modal split and direct demand models from Modelling Transport
- Discrete choice models from Modelling Transport
Disclaimer
Information on this site is purely for education purpose. The materials used and displayed on the Sites, including text, photographs, graphics, illustrations and artwork, video, music and sound, and names, logos, IS Codes, are copyrighted items of respective owners. Front Desk is not responsible and liable for information shared above.
2 Comments
[…] Mobility and Accessibility […]
[…] Mobility and Accessibility […]