- FORUM
- PROJECTS
- ABOUT US
- RESOURCES
- CONTACT US
- FORUM
- PROJECTS
- ABOUT US
- RESOURCES
- CONTACT US
TOD focuses on compact mixed use development around transit corridor such as metro rail, BRTS etc. International examples have demonstrated that though transit system facilitates transit oriented development, improving accessibility and creating walkable communities is equally important.
India’s National Transit Oriented Development (TOD) Policy was introduced in 2017 by the Ministry of Housing and Urban Affairs with the objective of promoting sustainable urban development and reducing congestion and pollution. Based on the objectives of National Urban Transport Policy, this TOD policy defines 12 Guiding Principles and 9 Supportive tools, as shown in Figure for realizing the objectives of TOD.
The policy outlines the following principles for TOD in India:
- Development density: The policy emphasizes the need for compact and dense development around transit corridors to reduce travel distances and encourage non-motorized modes of transport.
- Mixed-use development: TOD should encourage a mix of residential, commercial, and institutional land uses within walking distance of transit stations to promote activity and vitality in the area.
- Affordable housing: TOD should include provisions for affordable housing, including rental and social housing, to ensure that the benefits of transit access are accessible to all socio-economic groups.
- Walkability and public space: TOD should prioritize pedestrian and cycling infrastructure and public space design to create vibrant, safe, and comfortable streets for people.
- Public transport integration: TOD should integrate with the existing public transport network and be designed to facilitate intermodal transfers.
- Transit-oriented land use planning: TOD should be incorporated into the land use planning process at the city and regional level, and local authorities should provide incentives to encourage TOD development.
- Private sector engagement: The private sector should be engaged in the development and management of TOD projects through public-private partnerships to ensure financial sustainability and innovation.

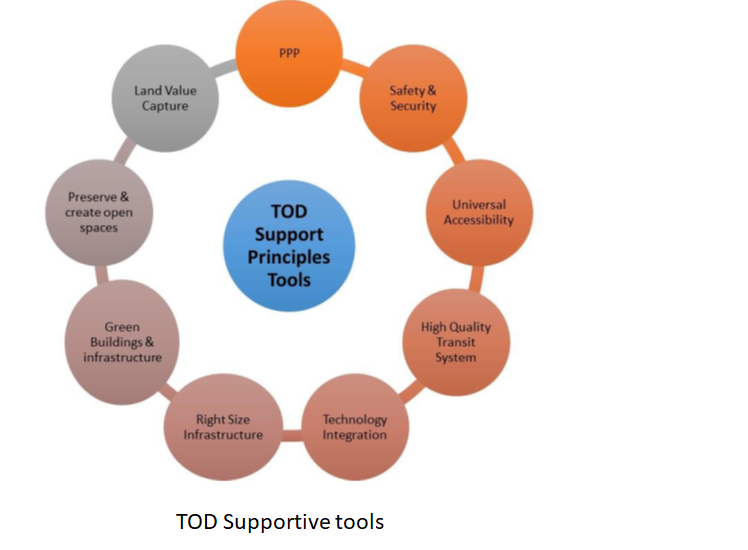
Principles of implementing TOD
Key principles for implementing TOD are :
1.Align human densities, economic densities, mass transit capacity, and transit network characteristics for greater accessibility.
2.Create compact regions with short commutes.
3.Ensure the resilience of areas connected by mass transit.
4.Plan and zone for mixed-use and mixed-income neighborhoods at a corridor level.
5.Create vibrant, people-centric public spaces around mass transit stations.
6.Develop neighborhoods that promote walking and cycling.
7.Develop good-quality, accessible, and integrated public transit.
8.Manage demand for private vehicles.
Approach for TOD Implementation National TOD policy
Land use and Transport Planning home page
Download Study Notes PDF
Land use and Transport Planning.pdf
Register as member and login to download attachment use this only for Educational Purpose
FD Planning Community Forum Discussion
- Land Use Transport Integration and Density of Urban Growth Toolkit
- Integration of Land Use and Transport Planning
- Introduction – Modelling Transport – Ortuzar Willumsen
- Mathematical Prerequisites from Modelling Transport
- data and space from Modelling Transport
- Trip Generation Modelling from Modelling Transport
- Modal split and direct demand models from Modelling Transport
- Discrete choice models from Modelling Transport
Disclaimer
Information on this site is purely for education purpose. The materials used and displayed on the Sites, including text, photographs, graphics, illustrations and artwork, video, music and sound, and names, logos, IS Codes, are copyrighted items of respective owners. Front Desk is not responsible and liable for information shared above.
1 Comment
[…] Principles of National TOD Policy […]