Artificial light sources are devices that produce light through the use of electricity or other means. They are used in a variety of applications, from general lighting in homes and offices to specialized lighting in industries such as automotive manufacturing, photography, and medicine. Here are some of the most common types of artificial light sources:
1 Incandescent lamps: The first incandescent lamp was in vented by Thoma Alva Edison in 1879 and comprise d carbon filaments instead of tungsten filaments. These lamps had an efficacy of 2.54 Im/W.
a. GLS (general lighting service) lamps
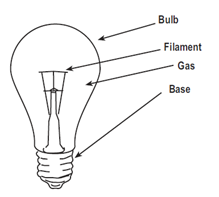
In these the light comes from a heated metal wire. The halogen lamp contains a special gas to improve the efficacy. These types are widely used, but will be phased out in the coming years due to their low efficacy;
These are the traditional light bulbs that have been used for many years. They work by passing an electric current through a filament, which heats up and emits light. However, incandescent lamps are not very energy-efficient, as a lot of the energy is wasted as heat.
GLS lamps consist of a tungsten wire filament on a suitable mount structure enclosed in a glass bulb containing an inert gas or vacuum.

b. Halogen Lamps

Halogen linear Lamp
In halogen lamps the bulb is filled with a halogen gas rather than nitrogen and argon. The halogen gas is either iodine or bromine, or in some cases a mixture of both. The bulb shape is tubular and its surface is closer to the hot filament
2.Gas Discharge lamps
In 1910 new category of light sources are used based on the principal of gas discharge. Gas discharge can be under low pressure or high pressure
- Low pressure mercury vapour lamp ( Fluorescent Lamp )
- CFL ( compact Fluorescent Lamp )
- HID (High Intensity Discharge ) lamp
- High pressure mercury vapour lamps (HPMV)
- Metal halide lamps (MH)
- High pressure sodium vapour lamps (HPSV)
- Low pressure sodium vapour lamps (LPSV)
Low pressure mercury vapour lamp (Fluorescent Lamp )
The light from these lamps, comes from a discharge between two electrodes in a gas tilled glass or ceramic tube. There are two ranges depending on the most important gas , mercury or sodium. Both these ranges can be subdivided by the pressure in the glass tube: high or low pressure
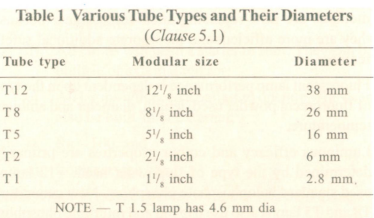
Fluorescent lamps have limited range of shapes , the most common is straight tube in various diameter ( Refer Table 1 ) .
Gas Discharge lamps Compact fluorescent lamps (CFLs).
These lamps work by passing an electric current through a gas or a mixture of gases, which produces light. Examples of gas discharge lamps include fluorescent lamps, compact fluorescent lamps (CFLs), and high-intensity discharge (HID) lamps. Fluorescent lamps are commonly used in commercial and residential lighting, while HID lamps are often used for outdoor lighting or in large indoor spaces such as warehouses.
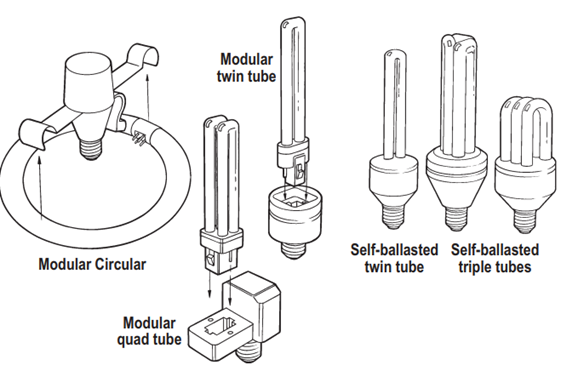
The new rare earth activated phosphor technology has led to the development of a growing variety of single ended lamps known as compact fluorescent lamps (CFLs). Several style of CFLs are shown in figure.
•Luminous efficacy of a typical CFL is 50–70 lumens per watt •Newer Compact fluorescent light bulbs give a warm, inviting light instead of the “cool white” light of older fluorescents.
HID (High Intensity Discharge ) High Pressure Mercury Vapour (HPMV) Lamps
The high pressure mercury vapour lamp was one of the first HID lamp types to appear on the market in 1930s. The outer bulb stabilizes and maintains the necessary high temperature around the arc tube and also absorbs the potentially hazardous UV radiation coming from the arc. Nitrogen gas within the outer bulb protects the metal parts from oxidation
luminous efficacy of around 50–65 lumens per watt,
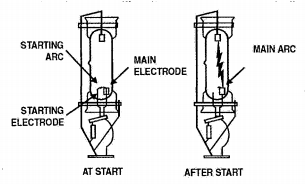
HMPV lamp operation
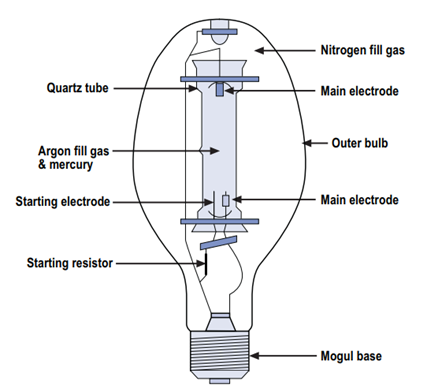
Adapted from IESNA Lighting Handbook
HID (High Intensity Discharge ) Metal Halide (MH) Lamps
Rapid technological changes have now made this group of lamps the most popular lamp both for indoor and outdoor applications. Its compact size and excellent colour properties make it suitable for a wide range of applications from sports to industry, cities and shops.
Metal halide lamps can broadly be grouped into 2 types, depending on the discharge tube material:
a)Quartz metal halides
b)Ceramic discharge metal halides
luminous efficacy of around 75–100 lumens per watt,
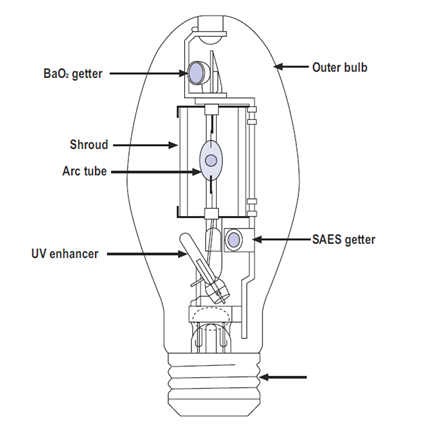
Adapted from IESNA Lighting Handbook
Application
HPI : Street lighting , Architectural lighting Sports field lighting
NaI-DyI3 : Sports field lighting
NaI -ScI3 : Shop lighting , Automotive headlights
3. Solid State Lighting LED (LIGHT EMITTING DIODES) light
LEDs are semiconductor diodes, which are electronic devices that permit current to flow in only one direction. The diode is formed by bringing two slightly different materials together to form p-n junction. In a p-n junction, the ‘p’ type contains excess positive charge (holes, indicating the absence of electrons) while the ‘n’ type contains excess negative charge (electrons).
When a forward voltage is applied to the semiconducting element forming the p-n junction, electrons move from the ‘n’ area toward the ‘p’ area and holes move toward the ‘n’ area. Near the junction, the electrons and holes combine. As this occurs, energy is released in the form of light that is emitted by the LED

An LED is a semiconductor device. When a current is passed through an LED, electrons move through the semiconductor material and some of them fall into a lower energy state . In the process, the ‘spare ‘ energy is emitted as light.
These lamps use a solid-state semiconductor material to produce light. They are highly energy-efficient, and have a longer lifespan than incandescent or gas discharge lamps. LED lamps are commonly used in residential, commercial, and outdoor lighting applications. They also come in a wide range of colors, making them useful for decorative lighting purposes.
In addition to the three main categories of artificial light sources there are also other types of artificial light sources that are used for specific lighting applications. Here are some examples:
- Halogen lamps: These are a type of incandescent lamp that use halogen gas to increase their efficiency and lifespan. They are often used for accent lighting, task lighting, and in automotive lighting.
- Neon lamps: These are gas discharge lamps that produce a glowing, neon-colored light. They are often used for advertising signs and displays.
- Electro-luminescent panels: These are thin, flexible panels that emit light when an electric current is passed through them. They are often used for backlighting in electronic displays and for decorative lighting purposes.
- Induction lamps: These lamps use electromagnetic induction to produce light. They are highly energy-efficient and have a long lifespan, and are often used for outdoor lighting and street lighting.
- Plasma lamps: These lamps use ionized gas to produce a bright, colorful light. They are often used for decorative lighting and as a novelty lighting source.
The choice of artificial light source will depend on factors such as the application, energy efficiency, lifespan, and cost.
Design of the lighting system : lumen method
Illumination in architecture – home page
FD Architect Community Forum Discussion
- Illumination – introduction
- Basic Terminology and Definitions
- Laws of Illumination The Inverse Square Law of Illuminance Illuminance (E) at any poi
- Laws of Reflection and Refraction
- Visual efficiency & comfort
- Day lighting
- Components of Daylight Factor
- Artificial Lighting Design
Download Study Notes PDF
Register as member and login to download attachment use this only for Educational Purpose
Disclaimer
Information on this site is purely for education purpose. The materials used and displayed on the Sites, including text, photographs, graphics, illustrations and artwork, video, music and sound, and names, logos, IS Codes, are copyrighted items of respective owners. Front Desk is not responsible and liable for information shared above.
2 thoughts on “Artificial light sources”