Lighting systems can be classified based on a variety of factors, including the type of light source being used, the purpose of the lighting, the level of control or automation, and the design approach. Here are some common classifications of lighting systems:
- General lighting vs. task lighting: Lighting systems can be classified based on their primary purpose. General lighting is used to provide overall illumination for a space, while task lighting is used to provide focused illumination for specific tasks.
- Natural vs. artificial lighting: Lighting systems can also be classified based on the source of light. Natural lighting comes from the sun and is often used to provide illumination during the day, while artificial lighting is produced by electric light sources and is used to provide illumination at all times.
- Ambient vs. accent lighting: Ambient lighting is used to provide overall illumination for a space, while accent lighting is used to highlight specific features or objects in a space.
- Manual vs. automated lighting: Lighting systems can be classified based on the level of control or automation. Manual lighting systems are controlled by switches or dimmers, while automated lighting systems use sensors or timers to adjust lighting levels based on occupancy, time of day, or other factors.
- Design-based classification: Lighting systems can also be classified based on the design approach used. For example, direct lighting is used to illuminate a specific area or object, while indirect lighting is used to illuminate a space by reflecting light off surfaces such as walls or ceilings.
These are just a few examples of how lighting systems can be classified. The specific classification used will depend on the context and purpose of the lighting system.
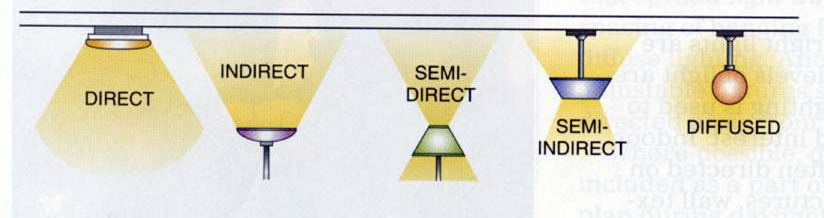
- Direct : Direct lighting fixtures are designed to provide illumination directly to a specific area or object.
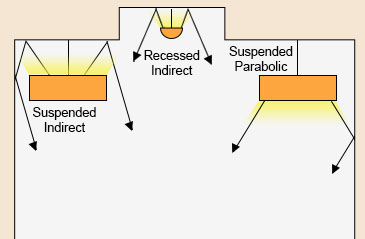
- Suspended parabolic : A suspended parabolic fixture is an example of a direct lighting fixture, where the light source is located within a parabolic reflector that directs the light downward. This type of fixture is commonly used in commercial settings such as offices, classrooms, and retail spaces.
- Indirect : Indirect lighting fixtures are designed to provide illumination by reflecting light off surfaces such as walls or ceilings.
- Suspended : Suspended and recessed fixtures are examples of indirect lighting fixtures. Suspended fixtures typically use a diffusing material to soften the light and provide even illumination throughout the space.
- Recessed : Recessed fixtures are installed into the ceiling and direct light upward, creating a diffuse and indirect illumination. Indirect lighting is commonly used in spaces where a soft and comfortable atmosphere is desired, such as lobbies, restaurants, and residential spaces.
- Semi direct
- Semi indirect
- Diffused
Illumination in architecture – home page
FD Architect Community Forum Discussion
- Illumination – introduction
- Basic Terminology and Definitions
- Laws of Illumination The Inverse Square Law of Illuminance Illuminance (E) at any poi
- Laws of Reflection and Refraction
- Visual efficiency & comfort
- Day lighting
- Components of Daylight Factor
- Artificial Lighting Design
Download Study Notes PDF
Register as member and login to download attachment use this only for Educational Purpose
Disclaimer
Information on this site is purely for education purpose. The materials used and displayed on the Sites, including text, photographs, graphics, illustrations and artwork, video, music and sound, and names, logos, IS Codes, are copyrighted items of respective owners. Front Desk is not responsible and liable for information shared above.
1 thought on “Classification of lighting system”