Dhundhar architecture is a regional architectural style that originated in the Dhundhar region of Rajasthan, India. The Dhundhar region includes the state capital, Jaipur, and its surrounding areas. This architectural style is closely associated with the city of Jaipur, which is known as the “Pink City” due to the predominant use of pink sandstone in its architecture.
Jeypore portfolio of architecture details by col. S. S. Jacob have extensive documentation of Dhundhar architecture style. Widely regarded as one of the chief proponents of the revival of building crafts in the region, as well as a leading exponent of the ‘Indo-Saracenic’ style, Jacob strove to adapt the building tradition to suit ‘modern’ requirements. The Portfolio was intended as a ‘practical’ reference to the architect and artisan in the form of ‘working drawings’ of these elements
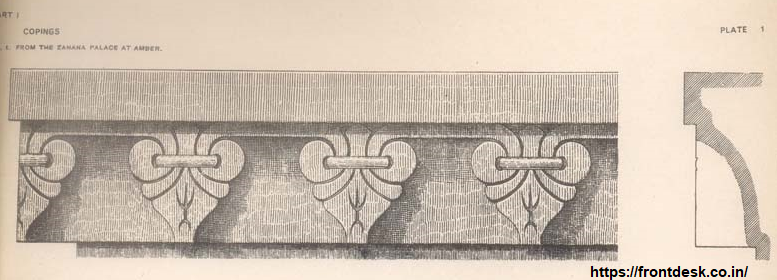
Amber was the former capital of the Dhundhar- now Jaipur Jayapur or Jeypore-State in Rajputana from about A.D. 1937 to A.D. 1798. It is 5 miles north of the present capital. It is almost entirely shut in by the surrounding hills, and is now nearly deserted. At the south end of the town is a small lake, and on its margin are the Royal Baths. From these a steep ascent leads up to the Fort or Castle, which contains the Old Palace. The Palace buildings were begun by Maharaja Mansingh about A.D. 1593, and were completed by Maharaja Sawai Jaysingh before the year A.D. 1728, when he removed the seat of Government to the modern capital. These buildings contain numerous courts and suites of apartments, some of them small and reached through intricate passages; others extremely beautiful, and “enjoying from their windows, balconies and terraces,” says Heber, one of the most striking prospects which can be conceived. For varied and pictureaque effect, for richness of carving, for wild beauty of situation, for the number and romantic singulanty of the apartments,” he adds, “I am able to compare nothing with Amber, and this, too, was the work of Jaysingh.” The Zanana Palace is part of the royal bundings in the Fort.
आमेर, जो करीब ई.स. 1798 तक ढूंढाड़ का पूर्व राजधानी था, अब जयपुर राज्य, राजपुताना का है। यह वर्तमान राजधानी से लगभग 5 मील उत्तर में है। यह कुछयत के पहाड़ों से लगभग पूरी तरह से घिरा हुआ है, और अब यह लगभग खाली हो गया है। नगर के दक्षिण अंश पर एक छोटा सा झील है, और इसके किनारे शाही स्नान घर हैं। इनसे एक ढीले चढ़ाई से किला या किला पर जाता है, जिसमें पुराना महल है। महल की निर्माण कार्य महाराजा मानसिंह ने करीब ई.स. 1593 को शुरू किया था, और इन्हें महाराजा सवाई जयसिंह ने ई.स. 1728 के बाद, जब उन्होंने सरकार की सीट को आधुनिक राजधानी में स्थानांतरित किया, पूरा किया। इन भवनों में कई आवास और अपार्टमेंट के सुइट हैं, जिनमें से कुछ छोटे हैं और जटिल पैसेज के माध्यम से पहुंचे जाते हैं; दूसरे बेहद सुंदर हैं, और “उनके खिड़कियों, बालकनियों और छतों से आनंद लेते हैं,” हीबर के अनुसार, “जो किसी भी प्राकृतिक दृश्य से भी अधिक प्रभावशाली है। विविध और चित्रण के लिए, नक्काशी की धनयता के लिए, स्थिति की जंगली सुंदरता के लिए, और आवासों की संख्या और रोमांचक अलगाव के लिए,” उनका यह कहना है, “मैं आमेर के साथ कुछ भी तुलना कर सकता हूँ, और यह भी, जयसिंह का काम था।” ज़नाना महल किले के शाही भवनों का हिस्सा है।
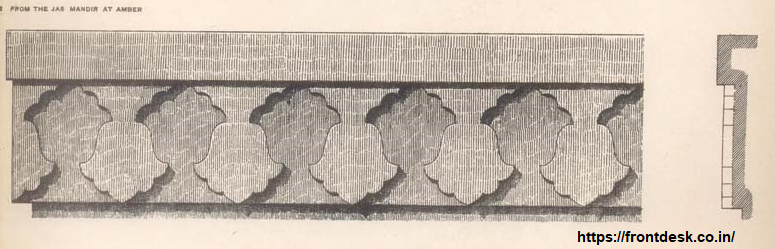
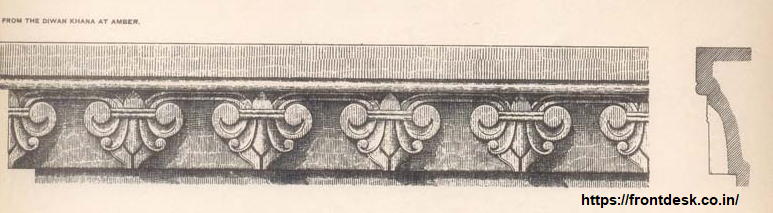
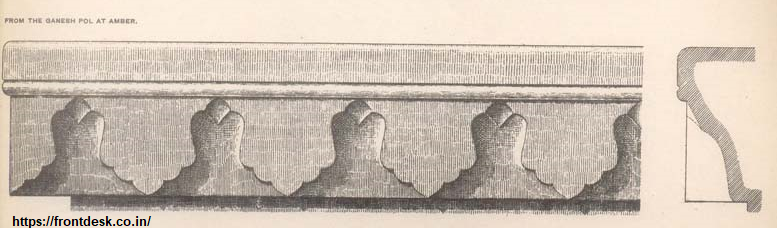
Dhundhar architecture is characterized by several distinctive features:
- Pink Sandstone: One of the most defining features of Dhundhar architecture is the use of pink sandstone, which gives the buildings in the region their unique appearance. The use of this sandstone is especially prominent in the old city of Jaipur.
- Symmetrical Layout: Dhundhar architecture often follows a symmetrical layout, with buildings and their components being balanced and harmonious in design. This symmetry is particularly evident in palaces and forts.
- Chhatris (Pavilions): Chhatris are small, elevated, dome-shaped pavilions that are commonly found in Dhundhar architecture. They are often used as memorials for royalty or as decorative elements in gardens.
- Jharokhas (Balconies): Jharokhas, or decorative enclosed balconies, are a common feature in Dhundhar architecture. They are adorned with intricate lattice work and often serve as vantage points to view processions or events.
- Courtyards: Traditional Dhundhar homes and havelis are built around central courtyards, which may include gardens, fountains, or other water features. These courtyards provide natural ventilation and serve as private spaces for residents.
- Frescoes and Murals: Some palaces and havelis in Dhundhar are adorned with colorful frescoes and murals that depict scenes from mythology, history, and daily life.
- Geometric Patterns: Dhundhar architecture often incorporates geometric patterns in its designs, both in the facades of buildings and in interior decor.
- Mughal Influence: While Dhundhar architecture has its own unique characteristics, it also shows the influence of Mughal architecture, especially in the use of arches, domes, and ornate decorative elements.
- Use of Local Materials: Like other regional architectural styles, Dhundhar architecture makes use of locally available materials, including sandstone and marble.
- Forts and Palaces: Dhundhar is home to several forts and palaces, with the Amber Fort being one of the most famous examples. These structures are known for their grandeur and architectural beauty.
Dhundhar architecture reflects the rich cultural heritage and historical significance of the region. It has contributed to the visual identity of Jaipur and remains a prominent attraction for tourists interested in exploring the architectural and cultural heritage of Rajasthan.
1 thought on “Dhundhar Architecture style ढूंढाड़ स्थापत्य शैली”