
Categories
Tags
2019 adi purana AutoCAD Drafting Building Bye Laws Building Regulation Building Services Commercial Cultural heritage Development Finance English Translation Event Forum Government Project heritage city Housing Illumination Interior Interior Design Resources Ishtopadesh Jainism Jaipur JDA Khandelwal Jain Samaj Land use and Transport Planning Model building bye laws 2025 Padmanandi Panchvinshatika Planning Planning Legislations Professional Practice Project Planning and Management PPM Projects Puja PurusharthSiddhiUpay Renovation Residential Scheme Solah karan vidhan Summary swadhyay Theory of Design urban development Management Urban Development Policies Urban Infrastructures & Network Vidhan Ward

1 Comment
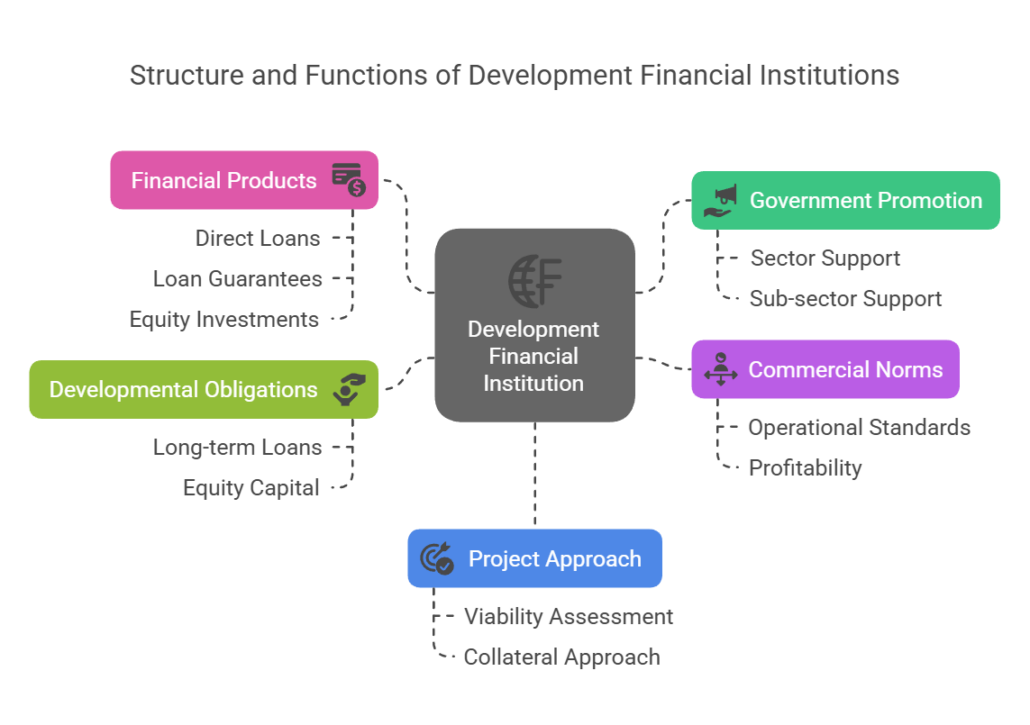
[…] Development Finance Institution […]