Monitoring is essential to get expected results of any development works. With monitoring comes evaluation automatically that can be employed to systematically measure and assess development work related activities.
Monitoring is the collection and analysis of information about a development project , undertaken while the project is ongoing.
The aim of monitoring is to ensure that the project is meeting its goals, objectives, and targets, and to make sure that it stays on track and within budget. It involves the collection and analysis of various data, such as project schedules, budgets, progress reports, quality control reports, risk assessments, and other relevant information that can help project managers make informed decisions and take corrective actions when necessary.
Evaluation is the periodic, retrospective assessment of an organization, project that might be conducted internally or by external independent evaluators.
Evaluation is the process of assessing and analyzing the results, impact, and effectiveness of a development project after it has been completed. The purpose of evaluation is to determine whether the project achieved its goals, objectives, and targets, and to identify the strengths and weaknesses of the project. Evaluation involves collecting and analyzing data and information to assess the project’s performance, effectiveness, and sustainability.
Action Research
A broader way of thinking about M&E is Action Research . Action Research is a term for a variety of methodologies that at their core are cycles of planning, action and reflection.
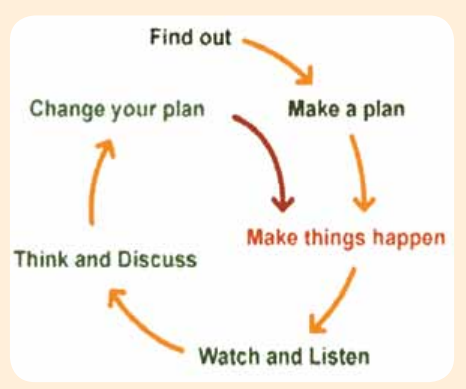
Action research is an approach to monitoring and evaluation that involves collaborating with stakeholders to identify and address problems and issues related to the development project. Action research is an iterative process that involves a series of cycles of planning, action, observation, and reflection. The aim of action research is to improve the effectiveness and impact of the project through continuous learning and adaptation.
In the context of monitoring and evaluation, action research can involve the following steps:
- Planning: Identify the research question, define the scope of the research, and identify the stakeholders who will be involved in the research process.
- Action: Implement the planned activities, such as data collection, analysis, and interpretation.
- Observation: Observe and document the results of the activities and identify any challenges or issues that arise.
- Reflection: Reflect on the results of the activities and identify ways to improve the effectiveness and impact of the project.
- Adaptation: Make changes to the project based on the results of the action research and implement the changes.
Action research can help to improve the monitoring and evaluation process by providing a framework for continuous learning and improvement. It can also help to build the capacity of stakeholders and encourage their participation in the evaluation process, leading to greater ownership and sustainability of the project.
Techniques of monitoring of development works – Cost control
Cost control is the process of comparing actual expenditures to the baseline cost plans to determine variances, evaluate possible alternatives, and take appropriate action. To effectively control costs, be sure cost plans are prepared with sufficient detail.
Cost control is the process of monitoring and managing expenses to ensure that a project stays within its budget. Effective cost control helps to maximize the value of the project by ensuring that resources are used efficiently and that costs are minimized without compromising quality.
The following are some key techniques for cost control:
- Planning: Developing a detailed project plan that includes a budget and a timeline is essential for effective cost control. The plan should include a breakdown of all costs and expenses associated with the project, and it should be updated regularly as the project progresses.
- Tracking and Reporting: Monitoring and reporting on project costs regularly is essential for effective cost control. This involves tracking all expenses, identifying any cost overruns, and reporting on the status of the project’s budget.
- Controlling Costs: Implementing measures to control costs is an important aspect of cost control. This may involve negotiating better pricing from suppliers, reducing unnecessary expenses, or finding ways to streamline processes and reduce waste.
- Risk Management: Risk management techniques such as identifying potential risks to the project and developing strategies to mitigate those risks can help to control costs by avoiding potential cost overruns or delays.
- Change Management: Changes to a project can often result in cost increases. Effective change management processes can help to manage changes to the project and minimize their impact on costs.
- Communication: Effective communication between project stakeholders is essential for effective cost control. This includes regular meetings, progress reports, and clear documentation to ensure that everyone is aware of the project’s budget and any cost-related issues.
By implementing these cost control techniques, project managers can ensure that a project stays within budget and that resources are used efficiently. Effective cost control can also help to maximize the value of a project by ensuring that it is delivered on time and within budget.
Works standard oriented cost control
Works standard oriented cost control is a method of cost control that is focused on achieving efficiency and cost savings through the implementation of standard operating procedures (SOPs) and best practices. The aim of works standard oriented cost control is to establish clear and consistent standards for work processes and activities, which can then be measured and improved over time to achieve cost savings.
The following are some key steps involved in works standard oriented cost control:
- Develop Standards: Develop clear and consistent standards for work processes and activities. These standards should be based on best practices and should be communicated clearly to all stakeholders.
- Measure Performance: Measure performance against the established standards to identify areas where improvements can be made. This may involve collecting data and analyzing it to identify trends and patterns.
- Analyze Variance: Analyze variances between actual performance and the established standards to identify the reasons for any deviations. This may involve conducting root cause analysis to identify underlying issues that are contributing to cost overruns.
- Implement Improvements: Implement improvements to work processes and activities based on the findings of the variance analysis. This may involve redesigning work processes, updating SOPs, or providing training to staff.
- Monitor Progress: Monitor progress over time to ensure that improvements are being sustained and that new issues are not emerging. This may involve regular reporting and review meetings to assess progress against established metrics and KPIs.
By implementing works standard oriented cost control, organizations can achieve cost savings through increased efficiency, reduced waste, and improved productivity. This approach can also help to improve the quality of work processes and activities, leading to better outcomes and higher customer satisfaction.
Inventory cost control technique
Inventory cost control is the process of managing and minimizing the cost associated with holding inventory. Effective inventory cost control techniques can help organizations to minimize the cost of holding inventory while ensuring that sufficient inventory is available to meet customer demand.
The following are some key techniques for inventory cost control:
- Inventory Analysis: Conducting regular inventory analysis is essential for effective cost control. This involves reviewing inventory levels, identifying slow-moving or excess inventory, and adjusting inventory levels as needed.
- Just-in-Time (JIT) Inventory: Implementing a just-in-time (JIT) inventory system can help to reduce inventory costs by minimizing the amount of inventory held on hand. JIT systems involve ordering inventory only as needed, which can help to reduce carrying costs.
- ABC Analysis: Conducting an ABC analysis of inventory can help to prioritize inventory management efforts. This involves classifying inventory items based on their value and importance, with high-value items receiving more attention than low-value items.
- Forecasting: Accurate forecasting of demand can help to ensure that the right amount of inventory is held on hand. This can help to reduce the cost of holding excess inventory and avoid stockouts.
- Supplier Management: Effective supplier management can help to minimize the cost of inventory by negotiating favorable terms with suppliers. This may involve negotiating lower prices, shorter lead times, or better payment terms.
- Lean Inventory Management: Implementing a lean inventory management system can help to reduce inventory costs by minimizing waste and improving efficiency. Lean systems involve eliminating unnecessary steps in the supply chain, reducing the amount of inventory held on hand, and improving inventory turnover.
Materials Management is related to planning, procuring, storing and providing the appropriate material of right quality, right quantity at right place in right time so as to co-ordinate and schedule the development activity in an integrative way for an development works. Effective management of materials can reduce these costs and contribute significantly to the success of the project Inventory technique Minimize of cost of entire project by controlling the inventory.
Inventory control pertains primarily to the administration of recognized policies, systems & procedures in order to reduce the inventory cost.
Inventory control technique Maintain sufficient stock of raw material in period of short supply and anticipate price changes.
By implementing these inventory cost control techniques, organizations can minimize the cost of holding inventory while ensuring that sufficient inventory is available to meet customer demand. Effective inventory cost control can help to improve profitability, reduce waste, and improve overall operational efficiency.
हिंदी Hindi
मॉनिटरिंग ( निगरानी )
मॉनिटरिंग किसी भी विकास कार्य के अपेक्षित परिणाम प्राप्त करने के लिए आवश्यक है। मॉनिटरिंग के साथ स्वचालित रूप से मूल्यांकन भी होता है जो विकास कार्य से संबंधित गतिविधियों का सिस्टमातिक रूप से मापने और मूल्यांकन करने के लिए किया जा सकता है।
मॉनिटरिंग वह प्रक्रिया है जिसमें विकास परियोजना के बारे में जानकारी का संग्रह और विश्लेषण किया जाता है, जो परियोजना जारी होने के दौरान किया जाता है।
मॉनिटरिंग का उद्देश्य यह सुनिश्चित करना होता है कि परियोजना अपने लक्ष्यों, उद्देश्यों और लक्ष्यों को पूरा कर रही है और यह सुनिश्चित करना होता है कि यह बजट के भीतर ही रहता है और ट्रैक पर रहता है। इसमें परियोजना संचालकों को सूचित निर्णय लेने और जब आवश्यक हो तब सुधारात्मक कार्रवाई लेने में मदद करने वाली विभिन्न डेटा का संग्रह और विश्लेषण शामिल होता है, जैसे परियोजना अनुसूची, बजट, प्रगति रिपोर्ट, गुणवत्ता नियंत्रण रिपोर्ट, जोखिम का मूल्यांकन और अन्य संबंधित जानकारी।
मूल्यांकन
मूल्यांकन संगणकीय, अंतर्निहित या बाह्य स्वतंत्र मूल्यांककों द्वारा किया जाने वाला एक संगठन, परियोजना का आवधिक, पूर्वावलोकन मूल्यांकन है।
मूल्यांकन परियोजना के पूरा होने के बाद उसके परिणाम, प्रभाव और प्रभावशीलता का मूल्यांकन और विश्लेषण करने की प्रक्रिया है। मूल्यांकन का उद्देश्य यह निर्धारित करना होता है कि परियोजना ने अपने लक्ष्यों, उद्देश्यों और लक्ष्यों को प्राप्त किया है या नहीं, और परियोजना की ताकतों और कमजोरियों की पहचान करना होता है। मूल्यांकन में डेटा और जानकारी का संग्रह और विश्लेषण शामिल होता है ताकि परियोजना के प्रदर्शन, प्रभावशीलता और विकास का मूल्यांकन किया जा सके।
Download Study Notes PDF
Register as member and login to download attachment use this only for Educational Purpose
FD Planning Community Forum Discussion
- State Finance Commissions and Rural Local Bodies Devolution of Resources
- Interview with B K Sinha – The Municipal midas
- Municipal bond in India
- Bilateral and Multi-lateral Financial Institutions
- Cost recovery
- Investment needs and Budgeting for Infrastructure and Service in Metro towns
- Subsidy Reduction
- Revenue Sources of Controlling Authorities
- Public Private partnership
Disclaimer
Information on this site is purely for education purpose. The materials used and displayed on the Sites, including text, photographs, graphics, illustrations and artwork, video, music and sound, and names, logos, IS Codes, are copyrighted items of respective owners. Front Desk is not responsible and liable for information shared above.

2 thoughts on “Techniques of monitoring of development works”