Traffic Impact Assessment or Traffic Impact Analysis (TIA) is the process of understanding the effect of the proposed project traffic on the existing surrounding and roads.
TIA is helpful in suggesting possibilities for linking the proposed project traffic to external roads with minimum interruption. With the rise in the number of private vehicles over the number of years in Indian Cities, it has become essential to understand the impact of any new development on its surroundings.
The term ‘Traffic Management’ represents the process of adjusting or adapting the use of an existing road system to meet specified objectives without resorting to substantial new road construction.
Important Terms :
Speed: The rate of motion or individual vehicles of a traffic stream. It is measured in meters per second or kilometers per hour.
Volume: The number of vehicles at a given point on a road during a designated time interval.
Time means Speed: It is the mean speed of vehicles observed at a point on the road over a period of time counts.
Space mean speed: It is the mean speed of vehicles in a traffic stream at any instant of time over a certain length of the road.
Density: It is the number of vehicles occupying in a unit length of a road at an instant of time. The unit length is generally one kilometer.
Capacity: It is defined as the maximum hourly volume (vehicle per hour) at which vehicles can reasonably be expected to traverse a point or uniform section of lane or roadways during a given time period under prevailing roadways, traffic and control conditions.
Peak hour factor: It is defined as the traffic volume during peak hour expressed as a percentage of average daily traffic. The peak hour volume in this case is taken as the highest hourly volume based on actual traffic
PCU – Passenger Car Unit or ECS – Equivalent Car Space: It is the unit used for the conversion of different types of vehicles on the road into a single unit for the ease of calculation of the capacity of the road as per Indian Road Congress.

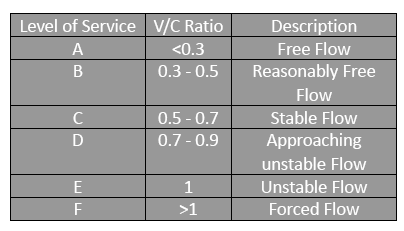
Volume-Demand-to-Capacity Ratio (V/C): It is a measure that reflects mobility and quality of travel of a facility or a section of a facility. It compares roadway demand (vehicle volumes) with roadway supply (carrying capacity). For example, a V/C of 1.00 indicates the roadway facility is operating at its capacity. It is a common performance measure and is widely used in transportation studies.
LoS – Level of Service : It is the measure of the current level of a particular infrastructure and direct representation of the Volume to Capacity Ratio, ranging from A to F.
VMT vehicle miles traveled : It measures the amount of travel for all vehicles in a geographic region over a given period of time, typically a one-year period. It is calculated as the sum of the number of miles traveled by each vehicle.
Traffic Impact Analysis (TIA) is a planning tool used to assess the potential transportation impacts of a proposed development or land use change. The primary goal of a TIA is to evaluate the potential effects of the proposed development on the surrounding transportation network, including roadways, intersections, and transit systems, and to identify potential mitigation measures to minimize adverse impacts.
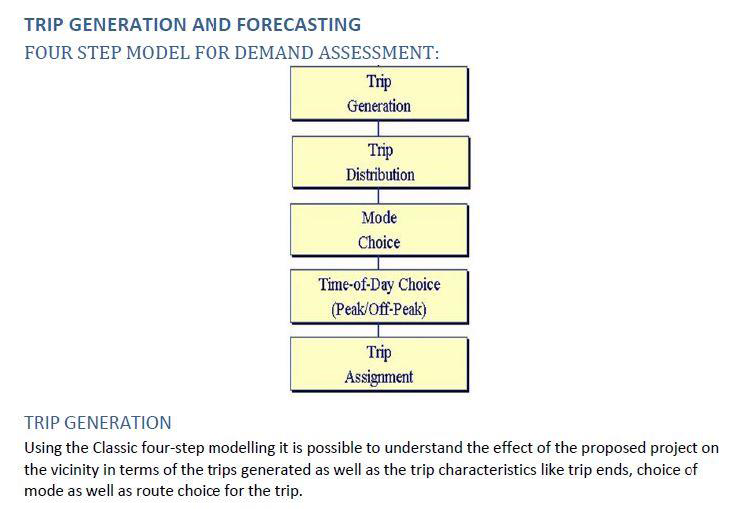
The TIA process typically involves several steps, including:
- IDENTIFICATION OF SITE CONTEXT AND ROAD INVENTORY : Identifying the proposed development or land use change, including its size, location, and intended use.
- TRAFFIC SURVEY : Collecting data on existing transportation conditions in the surrounding area, including traffic volumes, travel times, and transit service levels.
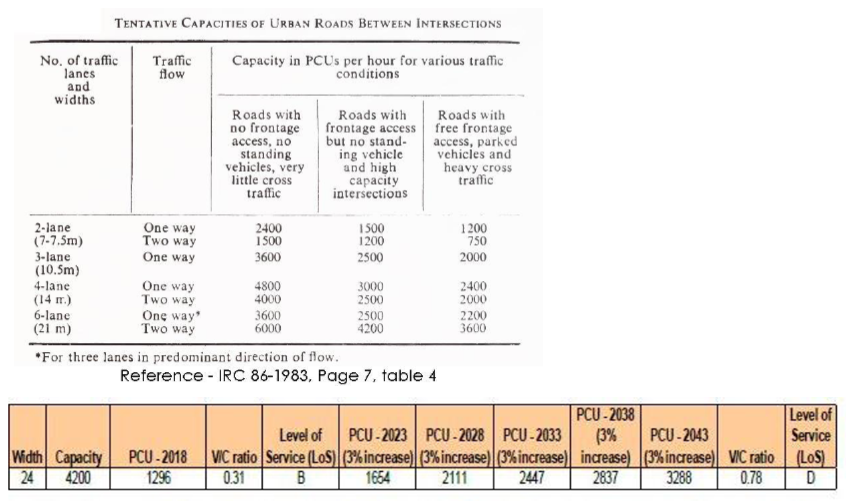
- PEAK HOUR TRAFFIC, CAPACITY ANALYSIS AND FUTURE PROJECTION : Using traffic engineering and transportation planning tools to estimate the additional traffic generated by the proposed development and its likely impact on the surrounding transportation network.
- ESTIMATING PEAK HOUR TRAFFIC GENERATED BY PROPOSED PROJECT
- ADDING THE PROJECT GENERATED TRAFFIC TO TRAFFIC PROJECTION
- Identifying potential mitigation measures to reduce any adverse impacts on the transportation network, such as roadway improvements, intersection modifications, or transit service enhancements.
- Evaluating the effectiveness of the proposed mitigation measures and making recommendations for their implementation.
Part 1: IDENTIFICATION OF SITE CONTEXT AND ROAD INVENTORY

The hierarchy in terms of the network of roads is to ensure scale and efficient circulation of traffic. To achieve this, through traffic routes are not be used for direct access to buildings or even to minor roads serving the buildings, because in that case not only the capacity of the through routes will be reduced but the intersections will also be unsafe.
The principal factors considered in designation roads into appropriate classifications are the existing and proposed land uses, overall travel demand, pattern of movement by various modes of transportation safety of traffic, environmental considerations etc. The major Arterial, Sub-arterial and Collector Roads need to be identified in order to calculate the exact traffic impact of the project.
Part 2: TRAFFIC SURVEY
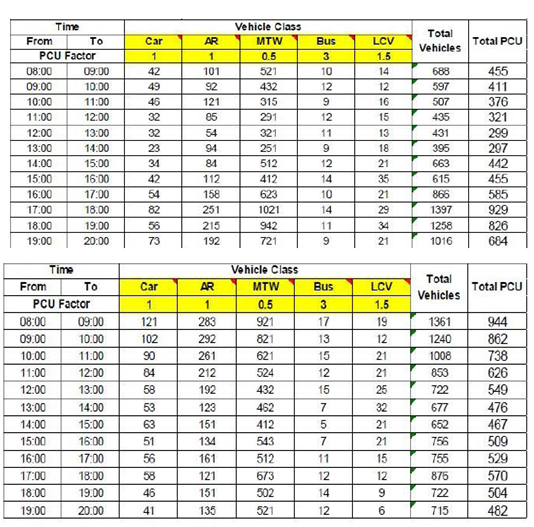
Part 3: PEAK HOUR TRAFFIC, CAPACITY ANALYSIS AND FUTURE PROJECTION
Part 4: ESTIMATING PEAK HOUR TRAFFIC GENERATED BY PROPOSED PROJECT
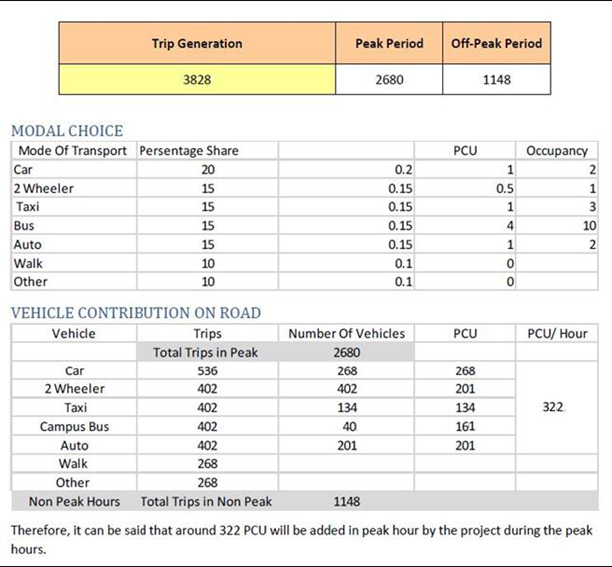
Part 5: ADDING THE PROJECT GENERATED TRAFFIC TO TRAFFIC PROJECTION

CONCLUSIONS
• The Level of Service on the proposed road is going from D (Approaching Unstable Flow) to E (Unstable Flow).
• Therefore, the project is seen to have adverse effect on the surrounding area traffic and mitigation measures have to be put in place for an efficient traffic management during and after the project construction.
The TIA report typically includes a summary of the proposed development, a description of existing transportation conditions in the surrounding area, the results of the traffic analysis, and a discussion of potential mitigation measures. The report may also include recommendations for future monitoring and evaluation to ensure that the proposed development does not have any unexpected transportation impacts over time.
The TIA process is an essential tool for ensuring that proposed developments and land use changes do not negatively impact the surrounding transportation network. By identifying potential transportation impacts early in the planning process and developing appropriate mitigation measures, the TIA process can help to ensure that new development is integrated effectively into the existing transportation infrastructure, minimizing any adverse impacts on the surrounding community.
Attributes used to measure the impact of land use on traffic
Land use and Transport Planning home page
Download Study Notes PDF
Land use and Transport Planning.pdf
Register as member and login to download attachment use this only for Educational Purpose
FD Planning Community Forum Discussion
- Land Use Transport Integration and Density of Urban Growth Toolkit
- Integration of Land Use and Transport Planning
- Introduction – Modelling Transport – Ortuzar Willumsen
- Mathematical Prerequisites from Modelling Transport
- data and space from Modelling Transport
- Trip Generation Modelling from Modelling Transport
- Modal split and direct demand models from Modelling Transport
- Discrete choice models from Modelling Transport
Disclaimer
Information on this site is purely for education purpose. The materials used and displayed on the Sites, including text, photographs, graphics, illustrations and artwork, video, music and sound, and names, logos, IS Codes, are copyrighted items of respective owners. Front Desk is not responsible and liable for information shared above.
1 thought on “Traffic Impact Analysis (TIA)”